Abstract
The method for the assay in mice of the α2 glycoprotein fraction of serum with immunosuppressive activity is described. The crude fraction has been shown to be effective in mice only with intravenous injection. When an antigen which is rapidly cleared from the blood is given, a single injection of the protein fraction given 10–20 hours before the exposure to antigen will inhibit the immune response in most animals. Time intervals outside this range are associated with a diminished or absent immunosuppressive effect.
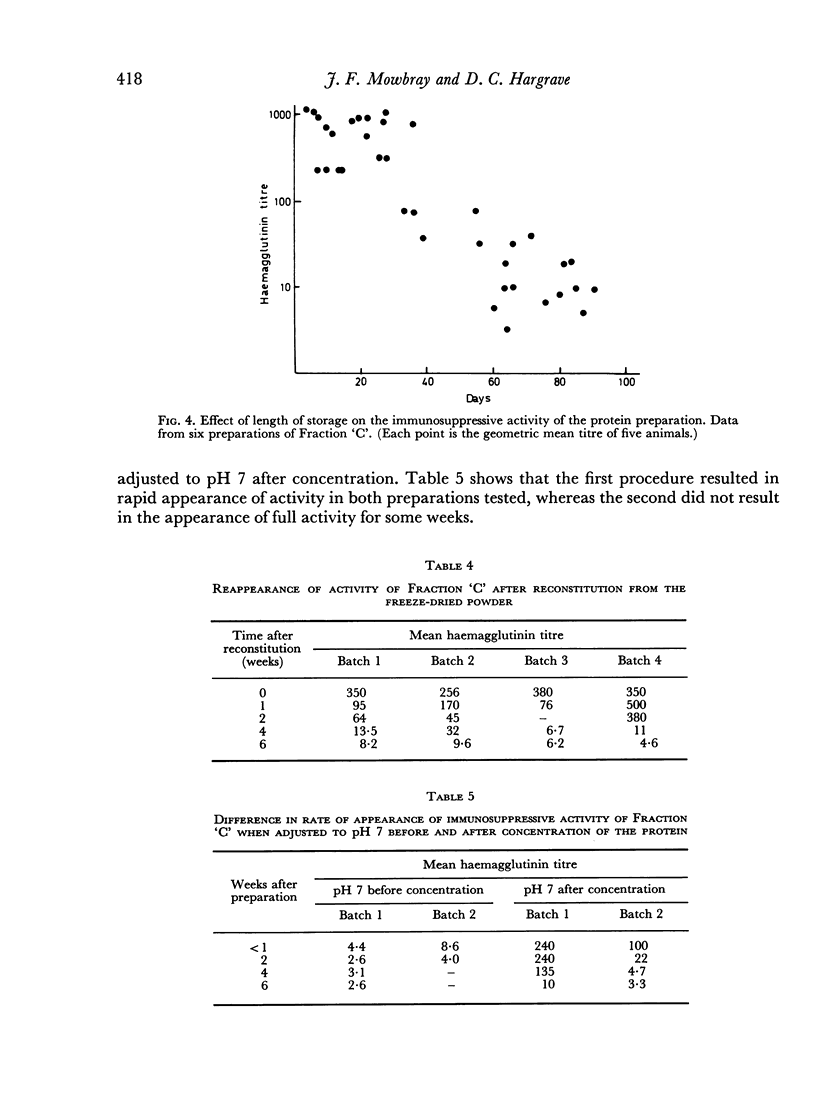
The protein fraction does not show activity immediately after preparation, or after reconstitution of freeze-dried material. Within 40 days, however, the activity is restored by storage alone, either frozen or at 4°. The presence of ribonuclease in the fraction is demonstrated, and its possible significance in relation to the immunosuppressive effect is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis W. C., Boxer L. A. Effect of alpha-2 glycoprotein on the immune response. Transplantation. 1965 Sep;3(5):673–676. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196509000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLISON P. L., VEALL N. The use of the isotope 51Cr as a label for red cells. Br J Haematol. 1955 Jan;1(1):62–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1955.tb05489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOWBRAY J. F. Ability of large doses of an alpha-2 plasma protein fraction to inhibit antibody production. Immunology. 1963 May;6:217–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIEGELBERG H. L., WEIGLE W. O. EFFECT OF AN ALPHA-2 GLOBULIN FRACTION ON ANTIBODY FORMATION IN RABBITS AND MICE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Nov;117:413–416. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



