Abstract
Thirty selected blood-group antibodies (excluding anti-A and anti-B) have been classified as β2M (19S γ) globulin, γ (7S γ) globulin or mixtures, using the following three methods: fractionation on a DEAE-cellulose column; indirect anti-globulin tests, using specific anti-β2M-globulin and anti-γ-globulin sera; and treatment with 2-mercapto-ethanol. With only minor exceptions, results obtained with the three methods were in agreement.
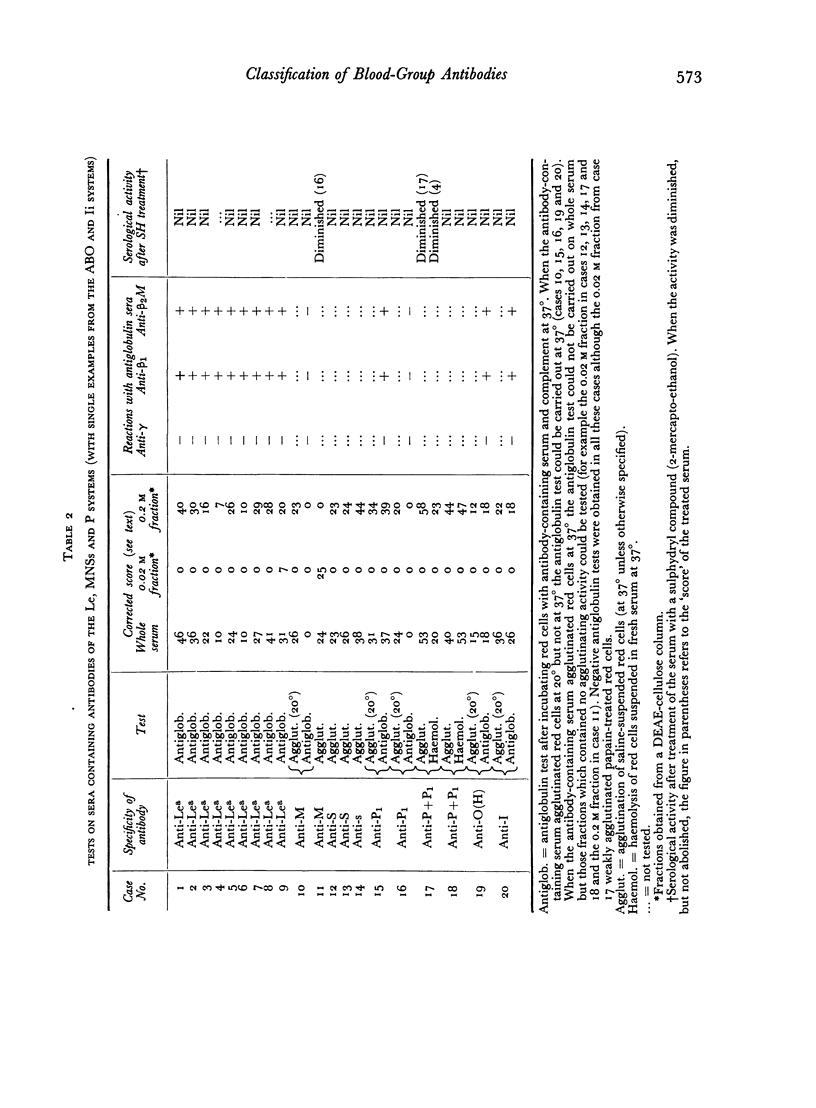
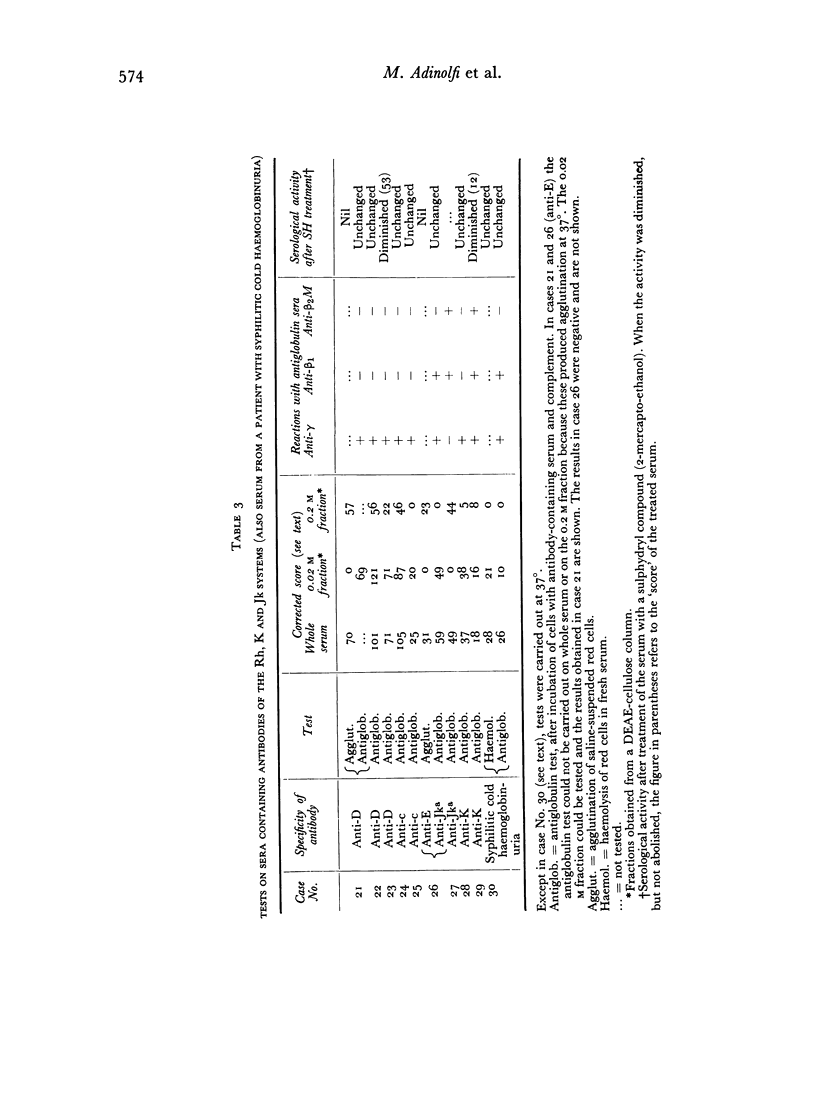
Most blood-group antibodies within the Le, MNSs and P systems appear to be `naturally occurring' and these were found to be β2M globulin. Blood-group antibodies within the Rh, K and Jk systems, which had arisen after an antigenic stimulus, were usually γ globulin but were occasionally β2M globulin.
Antibodies composed of β2M globulin usually behave as agglutinins but may behave as incomplete antibodies (e.g. some examples of anti-Jka); conversely, antibodies composed of γ globulin usually behave as incomplete antibodies but may behave as agglutinins (e.g. an example of anti-M).
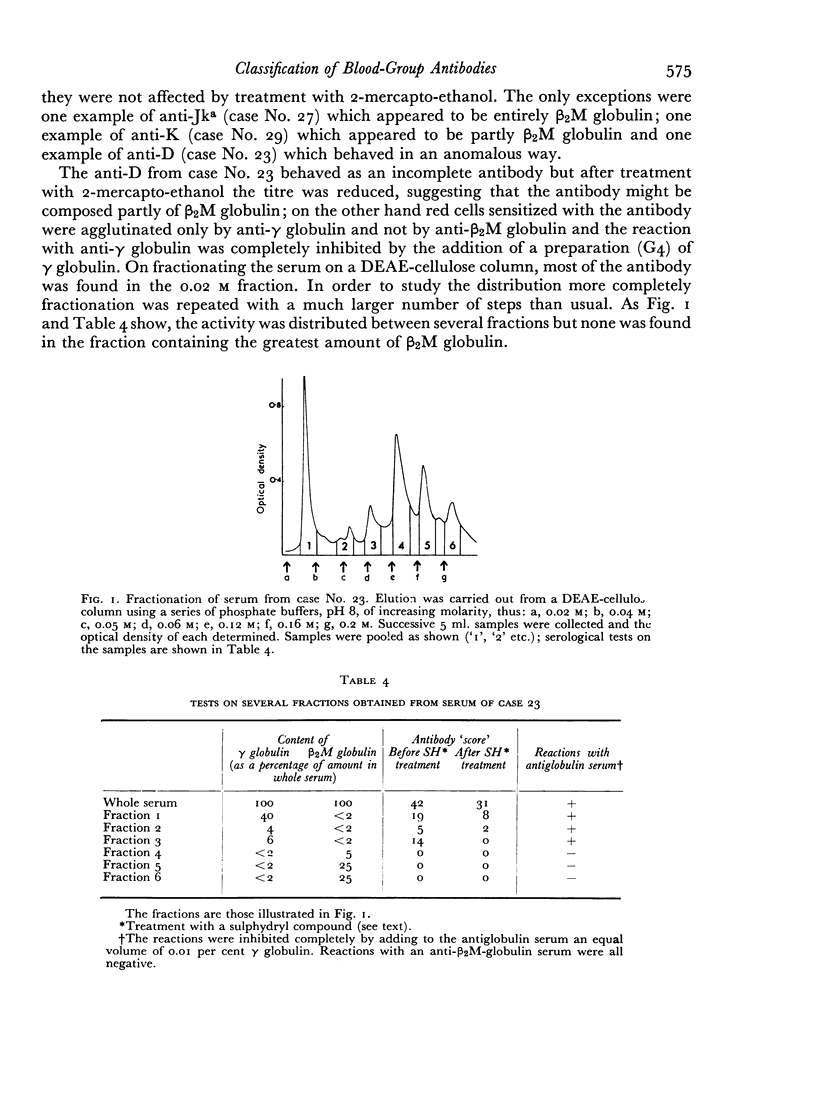
The ability to bind complement seems to be related more to the blood-group specificity of the particular antibody than to its molecular size. For example, anti-Jka, when composed either of γ or β2M globulin, seems invariably to bind complement, whereas potent anti-M or anti-Rh, whether composed of γ or β2M globulin, do not bind complement.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAMPBELL D. H., STURGEON P., VINOGRAD J. R. Separation of complete and incomplete Rh antibodies by centrifugation. Science. 1955 Dec 2;122(3179):1091–1092. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3179.1091-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUTBUSH M., GIBLETT E. R., MOLLISON P. L. Demonstration of the phenotype Le (a+ B+) in infants and in adults. Br J Haematol. 1956 Apr;2(2):210–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1956.tb06829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUTBUSH M., MOLLISON P. L. Relation between characteristics of blood-group antibodies in vitro and associated patterns of redcell destruction in vivo. Br J Haematol. 1958 Apr;4(2):115–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1958.tb03843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEUTSCH H. F., MORTON J. I. Dissociation of human serum macroglobulins. Science. 1957 Mar 29;125(3248):600–601. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3248.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., HORBETT A. P. Human gamma globulin fractionation on anion exchange cellulose columns. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2645–2651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEKWICK R. A., MOLLISON P. L. Blood group antibodies associated with the 19S and 7S components of human sera. Vox Sang. 1961 Jul;6:398–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1961.tb03186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEKWICK R. A., VALLET L., CUTBUSH M., MOLLISON P. L., THOMAS A. R., GELL P. G., SOOTHILL J. F. Estimation of gamma globulin in the serum of patients with hypogammaglobulinaemia. J Clin Pathol. 1961 Sep;14:470–477. doi: 10.1136/jcp.14.5.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'RIORDAN J., CANN J. Potent anti-s in pregnancy. Vox Sang. 1959 Jul;4:242–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1959.tb05134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLEY M. J., MOLLISON P. L., SOOTHILL J. F. The role of 19S gamma-globulin blood-group antibodies in the antiglobulin reaction. Br J Haematol. 1962 Apr;8:149–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1962.tb06507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAWSON A. J., ABELSON N. M. Studies of blood group antibodies. IV. Physicochemical differences between isoanti-A,B and isoanti-A or isoanti-B. J Immunol. 1960 Dec;85:640–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STONE B., MARSH W. L. Haemolytic disease of the newborn caused by anti-M. Br J Haematol. 1959 Oct;5:344–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1959.tb04044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


