Figure 1.
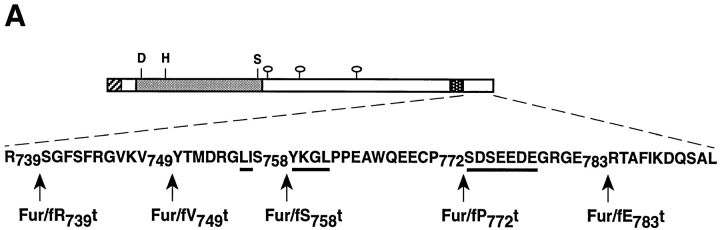
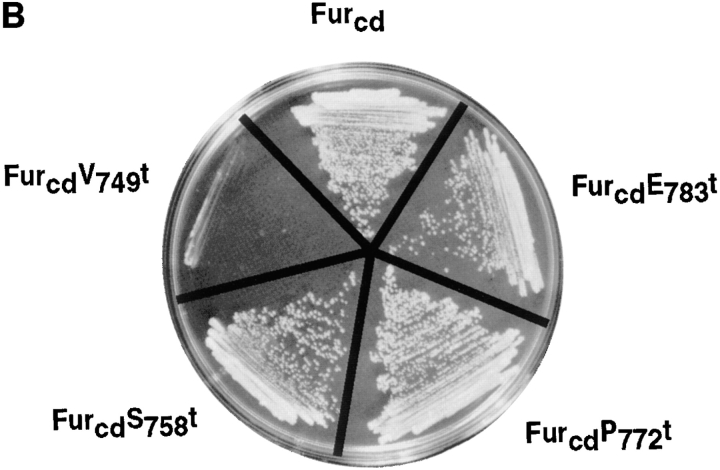
(A) Schematic of epitope-tagged furin (Fur/f) and COOH-terminal cytosolic domain truncated forms. The NH2-terminal cross-hatched box shows the FLAG epitope inserted COOH-terminal to the autoproteolytic maturation site (Molloy et al., 1994). The FLAG epitope cross-reacts with both mAbs M1 and M2. Binding of the mAb M1 requires the free amino terminus of the FLAG tag, whereas mAb M2 does not. Because autoproteolytic cleavage of the furin propeptide is localized to the RER (Molloy et al., 1994), all furin molecules trafficking in the TGN/endosomal compartments are capable of binding both mAbs. The lightly shaded area represents the catalytic domain with the Asp (D), His (H) and Ser (S) residues that form the catalytic triad, the hooked ovals represent NH2-linked carbohydrates and the dark-stippled box represents the membrane spanning domain. The sequence of the 56-amino acid cd is shown including the location of each of the COOH-terminal truncation sites. The Tyr-based and di-leucine-like internalization motifs, as well as the acidic cluster necessary for TGN localization of furin are underlined. (B) Two-hybrid analysis of furin cd truncations (bait), with library clone TP107, is identified in the initial screen. Yeast cells were cotransformed with pTP107 (Leu− medium) and bait plasmids (Trp− medium) expressing either furin cd or one of the furin cd truncation mutants (A) and selected for growth on Leu−/Trp− medium. Colonies from the Leu−/Trp− plates were streaked onto His- plates and scored for growth.