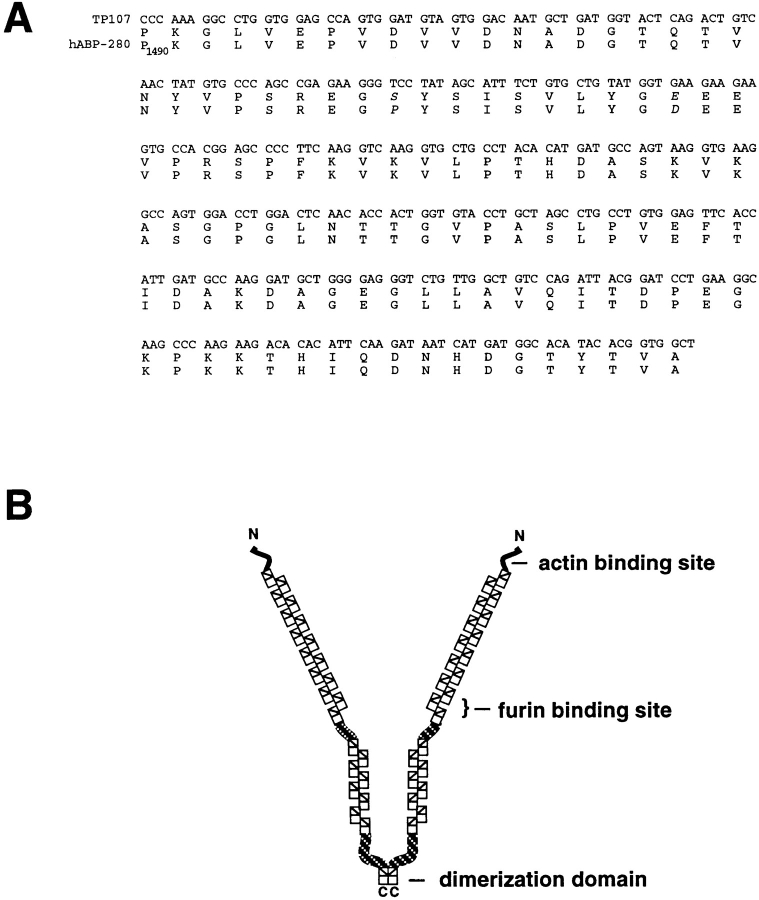
Figure 2.
Identification of TP107 as mouse ABP-280. (A) Alignment of TP107 and ABP-280. Shown are the nucleic acid sequence for the TP107 insert (top), the corresponding TP107 open reading frame (middle), and the amino acid sequence of the corresponding region of human ABP-280 (Gorlin et al., 1990). Species-specific amino acid changes are shown in italics. (B) Schematic of ABP-280. ABP-280 is a homodimer composed of two 280-kD subunits, each of which contains an amino-terminal actin binding domain followed by 24 repeats of a structurally conserved 96-amino acid β-sheet structure (rectangles). Hinge regions are located between repeats 15/16 and 23/24. The centrally placed hinge region permits the orthogonal positioning of cortical microfilaments required for the “sol-gel” transition states of cytosol, as well as the formation of lamellapodia necessary for cell crawling. The COOH-terminal 24th repeat contains the ABP-280 dimerization domain. Alignment of TP107 with the reported sequence for human ABP-280 shows that it is contained within the region bridging the 13th and 14th repeats (residues 1490–1607 in human ABP-280).