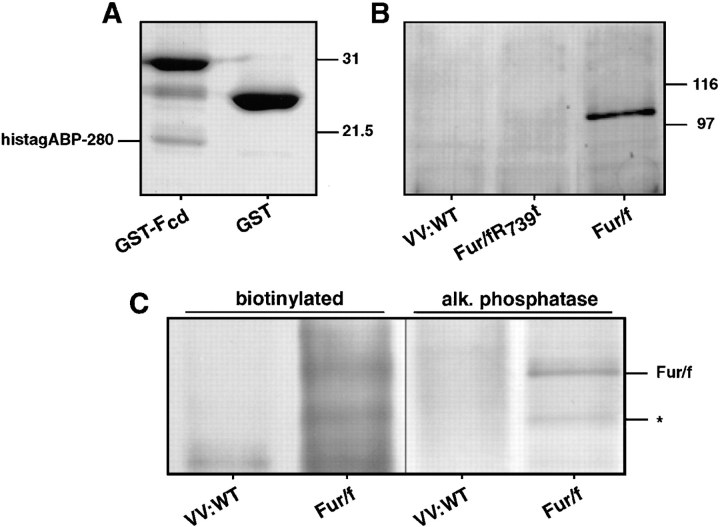
Figure 3.
Interaction of ABP-280 and furin. (A) Binding in vitro of HistagABP-280 to GST-furin cd. 6 μg of a His-tagged construct containing residues 1490–1607 of mouse ABP-280 was combined with 10 μg of GST or a GST fusion protein containing the entire furin cd (GST-Fcd). Glutathione agarose was then added and bound proteins were removed from the washed beads with SDS-sample buffer and separated by SDS-PAGE (10% acrylamide). Proteins were detected by staining the gel with Coomassie Blue R250. The positions of molecular weight standards are shown on the right. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of ABP-280 and fur/f. Replicate plates of BSC-40 cells were infected with wild-type vaccinia virus or vaccinia recombinants expressing either fur/f or the furin cd truncation mutant fur/fR739t depicted in Fig. 1 (moi = 5). At 16 h after infection, the cells were harvested and the clarified cell extracts were incubated overnight with the anti– filamin(ABP-280) mAb (Gorlin et al., 1990). Samples were then treated with protein G Sepharose and bound proteins dissolved in SDS-sample buffer, separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose. Coimmunoprecipitating FLAG epitope-tagged furin constructs were detected by incubating the blot with mAb M1. Parallel plates of total cell extract show that equivalent amounts of mAb M1 immunoreactive fur/f constructs were expressed in each sample (data not shown). The positions of molecular weight standards are shown on the right. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of ABP-280 with cell surface fur/f. Parallel plates of BSC-40 cells were infected with either wild-type vaccinia virus or the recombinant expressing fur/f. At 6 h after infection, the cells were placed on ice and cell surface molecules were biotinylated as described in Materials and Methods. The cells were then harvested and subjected to immunoprecipitation with the anti–ABP-280 mAb as described in B. The immunoprecipitates were boiled in mRIPA containing 1% SDS, diluted 10-fold in buffer, and furin molecules immunoprecipitated with the anti–furin cd antiserum. The immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and biotinylated proteins were detected by chemiluminescence (left). The blot was then reprobed with the anti–furin cd antiserum and developed with alkaline phosphatase (right). 100 kD fur/f is marked. The smaller 82 kD biotinylated furin protein (*) represents a degradation product of the endoprotease, generated under these conditions, that still contains the intact cytosolic domain.