FIGURE 2.
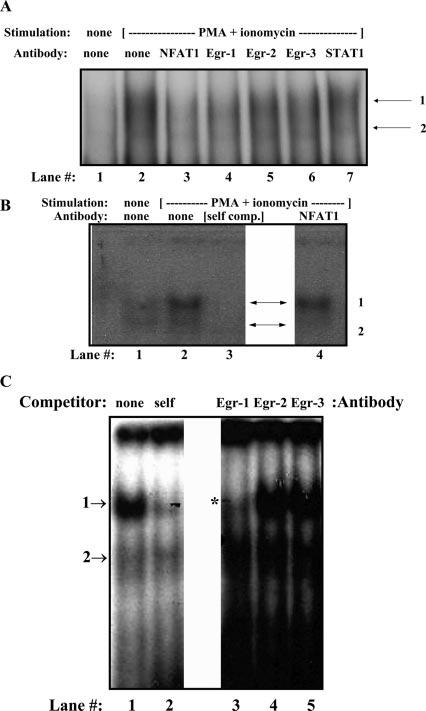
Egr-1 binds the proximal hCD154 promoter in vitro. Nuclear extracts from resting (A, lane 1) or polyclonally activated Jurkat (A) and primary human CD4 T cells (B and C) were incubated with an oligo-nucleotide probe encompassing the hCD154 proximal promoter NFAT and Egr sites. This resulted in the formation of two complexes (arrows) in activated extracts as seen in A (lane 2), B (lane 2), and C (lane 1). Both complexes were partially inhibited by excess self, cold probe (B, lane 3; C, lane 2). The upper complex (C, *) was specifically inhibited by an anti-Egr-1 Ab (A, lane 4; C, lane 3) but not by Abs to Egr-2 (A, lane 5; C, lane 4), Egr-3 (A, lane 6; C, lane 5), or STAT1 (A, lane 7). Anti-NFAT1 also inhibited upper complex formation in Jurkat extracts (A, lane 2) but primarily blocked lower complex formation in primary CD4 T cell extracts (B, lane 4).
