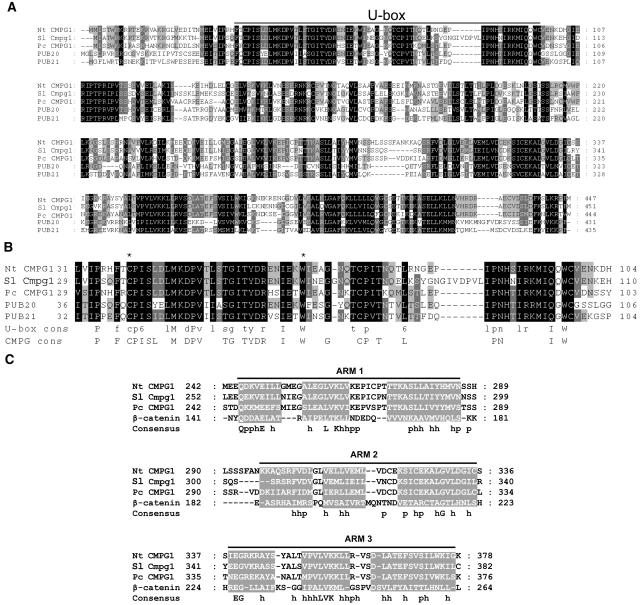
Figure 1.
Sequence of Nt CMPG1 Protein and Alignment with Homologs.
(A) Protein sequence comparison between tobacco Nt CMPG1, tomato Sl Cmpg1, parsley Pc CMPG1, and Arabidopsis PUB20 and PUB21 was performed using ClustalW software. Position of the U-box domain is indicated. Shading represents the conservation of the residues among the sequences of the alignment: black, the residue is conserved in all the sequences; dark gray, the residue is conserved in four proteins of the alignment; light gray, the residue is conserved in three proteins of the alignment.
(B) Protein sequence alignment of the U-box domain of Nt CMPG1 homologs and comparison with U-box and CMPG consensus sequences. Asterisks show the amino acid residues mutated in this work to generate the dominant-negative versions of Nt CMPG1.
(C) Protein sequence comparison between the ARM repeats of Nt CMPG1, Sl Cmpg1, Pc CMPG1, and β-catenin (from human). The gray boxes indicate the protein region where an α-helix secondary structure was predicted. The consensus sequence is indicated, where p indicates polar residue and h indicates hydrophobic residue.