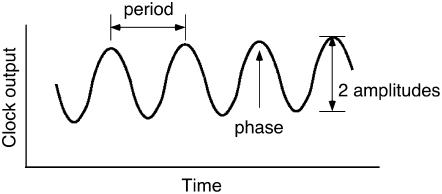
Figure 1.
Critical Terms Used to Describe Circadian Rhythms.
Period is defined as the time to complete one cycle. It is commonly measured from peak to peak but could equally be measured from trough to trough or from any specified phase marker. Phase is the time of day for any given event. For example, if the peak in a rhythm occurred at dawn, the phase of the peak would be defined as 0 h. If a rhythm peaked 6 h after dawn, its phase would be 6 h, and so on. Phase is often defined in zeitgeber time (ZT). Zeitgeber is German for time giver, and any stimulus that imparts time information to the clock is a zeitgeber. The onset of light is a powerful zeitgeber, and dawn is defined as ZT0. The amplitude of the rhythm is defined as one-half the peak-to-trough distance.