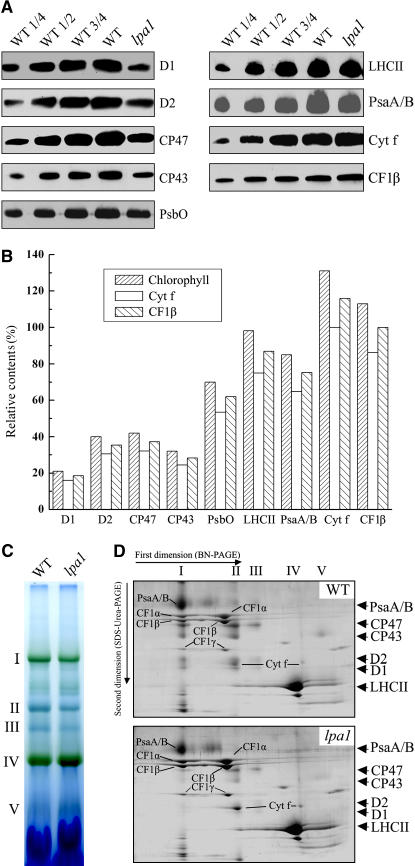
Figure 4.
Analysis of Thylakoid Membrane Proteins from lpa1 and Wild-Type Plants.
(A) Immunodetection of chloroplast proteins. The thylakoid membrane proteins were separated by SDS-urea-PAGE, and the blots were probed with specific anti-D1, anti-D2, anti-CP43, anti-CP47, anti-PsbO, anti-LHCII, anti-PsaA/B, anti-cytochrome f, and anti-CF1β antibodies.
(B) Semiquantitative analysis of chloroplast proteins. X-ray films were scanned and analyzed using an AlphaImager 2200 documentation and analysis system. The protein contents (per unit of chlorophyll) of the thylakoid membrane were determined and compared. The signal intensities of the immunoblot of the mutant, relative to those in the wild type, were also normalized to the cytochrome f and CF1β blot signals.
(C) BN gel analysis of thylakoid membrane protein complexes. Thylakoid membranes (10 μg chlorophyll) from wild-type and lpa1 mutant leaves were solubilized with 1% dodecyl-β-d-maltoside and separated by BN gel electrophoresis. The positions of protein complexes were identified with appropriate antibodies (see Guo et al., 2005).
(D) Two-dimensional separation of protein complexes in the thylakoid membranes. BN-PAGE–separated thylakoid proteins in a single lane from a BN gel were separated in a second dimension by 15% SDS-urea-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. Names of the proteins resolved by the second dimension SDS-PAGE, identified by immunodetection and matrix-assisted laser-desorption ionization time of flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry, are indicated by arrows.