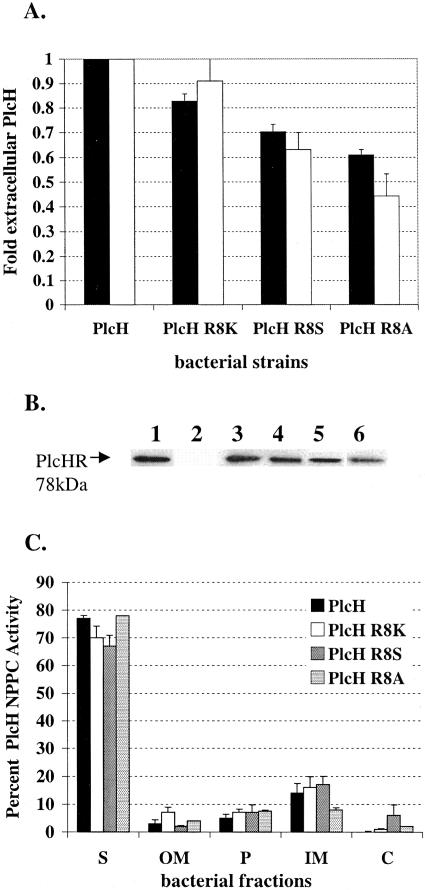
FIG. 3.
The PlcH R8K, PlcH R8S, and PlcH R8A signal sequence mutants are not affected in secretion but produce less total PlcH. (A) PlcH in supernatants of ADD1976 expressing wild-type PlcH or the PlcH signal sequence mutants was measured by detecting NPPC activity (black bars) and by quantitation of total extracellular PlcH protein by immunoblot analysis (white bars). Wild-type PlcH NPPC activity (calculated as 100 × ΔOD590/Δtime) and total wild-type extracellular PlcH protein concentration were set to 1, and the PlcH activity and PlcH protein concentration detected in the supernatants of each mutant were compared to this standard. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means of three independent experiments. (B) Total PlcH protein in supernatants by immunoblot analysis. Lane 1, purified PlcH control; lane 2, ADD1976 with the vector; lane 3, ADD1976 with wild-type PlcH; lane 4, ADD1976 with PlcH R8K mutant; lane 5, ADD1976 with PlcH R8S mutant; lane 6, ADD1976 with PlcH R8A mutant. The arrow in lane 1 shows the twin Arg signal peptide. (C) Distribution of bacteria-associated PlcH activity. Bacterial pellets of ADD1976 expressing wild-type PlcH or PlcH signal sequence mutants were fractionated into OM, P, IM, and C as described in Materials and Methods. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means of three independent experiments. S, supernatant.