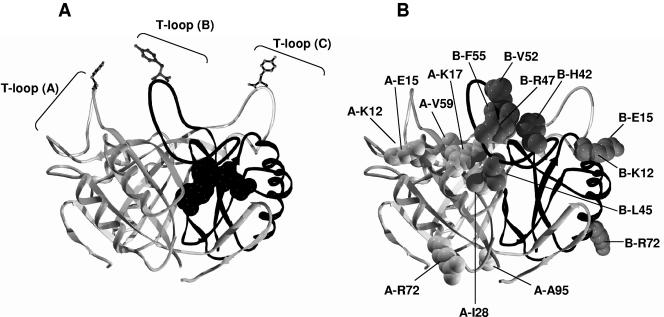
FIG. 1.
Model of the structure of R. rubrum GlnB. (A) Ribbon model of the E. coli GlnB trimer (6). The B monomer is shown with a dark backbone. A single ATP molecule, whose position is based on the structure of ATP-bound GlnK of E. coli (60, 61), is shown at the interface of monomers A and B. The T loops are indicated, and at the tip of each is Tyr51, the site of uridylylation. (B) The same view, but with the R. rubrum wild-type residues altered in the GlnB* variants shown as space filled. Only residues on one face of the trimer are shown, and their respective monomer is indicated by the “A” or “B” preceding the residue name.