FIG. 4.
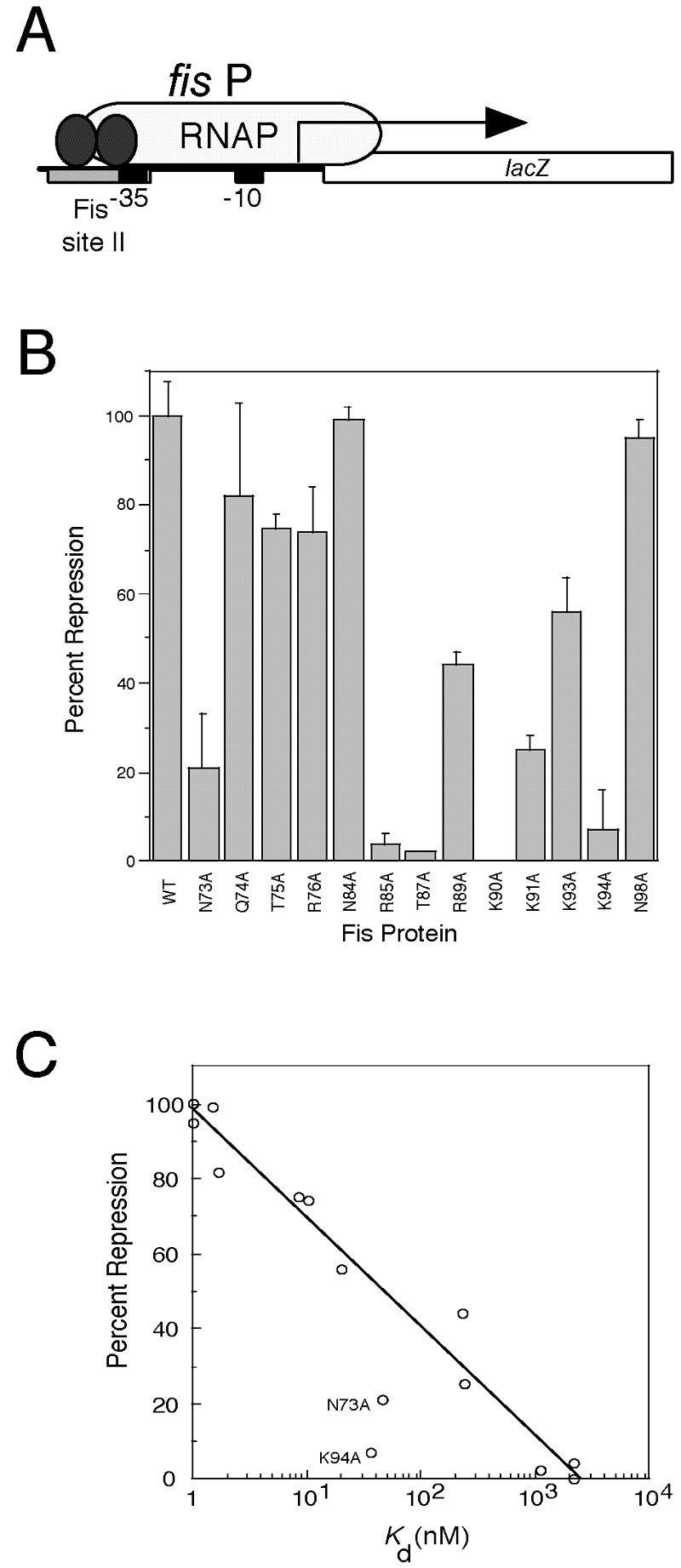
Effect of Fis mutations on fis P II site-mediated repression in vivo. (A) Schematic diagram of the fis promoter::lacZ fusion used in the repression assay. The fis promoter (fis P) region from position −83 to position +5, which carries the fis P II Fis site centered at position −44 (gray rectangle), the fis P −35 and −10 regions (black boxes), and the fis P transcription initiation region (arrow), is fused to lacZ and placed as a single copy in the chromosome. Fis (two ellipses) binds to the single fis P II site to hinder RNA polymerase (RNAP) binding and cause transcription repression. (B) Relative fis P repression activities of the Fis mutants used in this study. The percentages of repression are calculated from β-galactosidase activity measurements and are averages for at least three independent assays; the error bars indicate standard deviations. (C) Correlation (R = 0.98) between the percent repression and the logarithm of Kd app from the in vitro binding to fis P site II for the majority of the Fis proteins. The exceptions were the values for N73A and N94A, which deviated significantly from the curve and are labeled.
