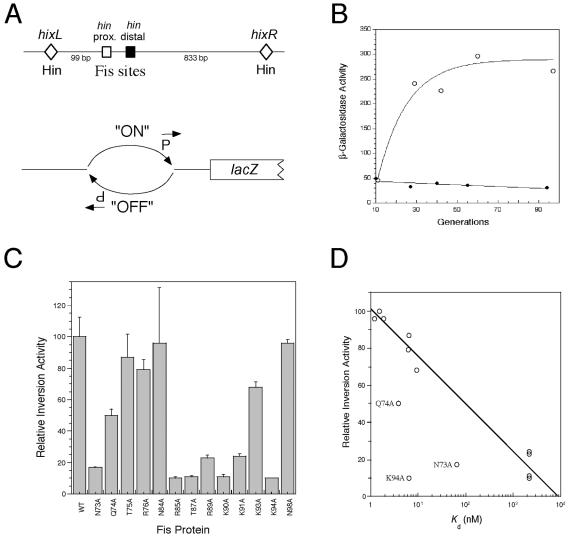
FIG. 6.
Effect of Fis mutations on stimulation of hin-mediated DNA inversion in vivo. (A) Schematic diagrams of the hin inversion region. The top diagram shows the relative positions of the hixL and hixR Hin binding sites (diamonds) and the proximal (open square) and distal (solid square) Fis binding sites. Distances (in bp) between hixL and the proximal Fis site and between hixR and the distal Fis site are indicated. The lower diagram shows the λ fla406 construct on the E. coli chromosome used in the in vivo Hin-mediated DNA inversion assay. The promoter located within the invertible DNA segment is initially in the “OFF” position. In the presence of Hin and functional Fis, the DNA is inverted to the “ON” position and lacZ is expressed. (B) Effect of Fis on Hin-mediated DNA inversion in vivo. E. coli strain RJ2539 (λ fla406 ‘off’) was transformed with either pRJ807 (○) or pRJ1122 (•) and grown for up to 96 generations. The results of β-galactosidase assays performed at various times after growth were plotted against the number of generations. (C) Relative DNA inversion stimulation by WT and mutant Fis. The DNA inversion activity relative to WT Fis after 52 to 56 generations was calculated as described in Material and Methods. The results are averages from three experiments, and the error bars indicate standard deviations. (D) Correlation (R = 0.98) between the relative inversion activity and the logarithm of Kd from the in vitro binding activity to the hin distal Fis site for the majority of the Fis mutants. The exceptions are the values for N73A, N94A, and Q74A, which deviated significantly from the curve and are labeled.