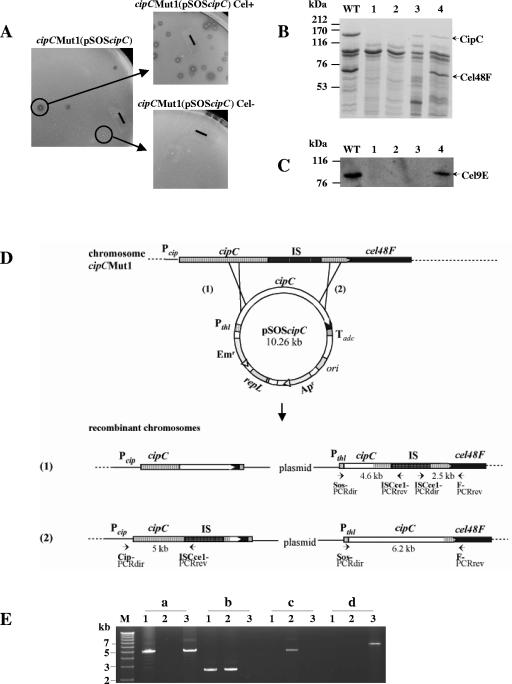
FIG. 1.
Recombinant cipCMut1(pSOScipC) clone analysis. (A) Phenotype of cipCMut1(pSOScipC) stains. A cellulolytic strain (Cel+) was selected from the cipC trans-complemented cipC mutant strain cipCMut1(pSOScipC) on cellulose-containing solid medium. The solid bars correspond to 6 mm. (B) SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis and (C) Western blot analysis with antiserum raised against Cel9E of the Fc fraction from wild-type (lane WT), cipCMut1 (lane 1), cipCMut1(pSOSzero) (lane 2), cipCMut1(pSOScipC) Cel− (lane 3), and cipCMut1(pSOScipC) Cel+ (lane 4) strains. (D) Schematic representation of possible homologous recombination events between the mutated chromosomal cipC gene and the wild-type plasmidic cipC gene. Pcip, promoter region of the cipC gene; IS, insertion element ISCce1::ISCce2 (15); Pthl, promoter region of the constitutive thiolase gene and Tadc, transcriptional terminator region of the acetoacetate decarboxylase gene. Both Pthl and Tadc are from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 (30). Small solid arrows show primers used for PCR analysis. (E) PCR analysis of cipCMut1(pSOScipC) recombinant clones followed by 0.7% agarose gel electrophoresis. PCR was carried out with primers Cip-PCRdir and ISCce1-PCRrev (a), ISCce1-PCRdir and F-PCRrev (b), Sos-PCRdir and ISCce1-PCRrev (c), and Sos-PCRdir and F-PCRrev (d) with 20 ng of genomic DNA of cipCMut1 (lanes 1), cipCMut1(pSOScipC) Cel− (lanes 2), and cipCMut1(pSOScipC) Cel+ (lanes 3). The fragments of 15.3, 12.5, and 8.9 kb, expected in lanes a2, b3, and d2, respectively, are too large to be synthesized by PCR with the Expand long template PCR system (Roche Applied Science). M, DNA molecular weight marker X (Roche Applied Science).