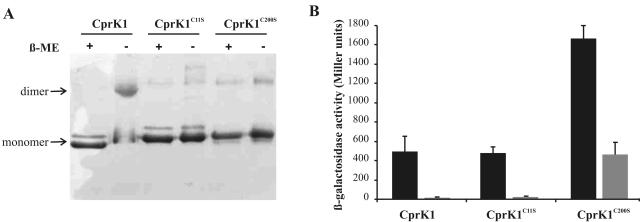
FIG. 8.
Effect of redox state of CprK1 on its activity. (A) SDS-PAGE gel of purified wild-type CprK1, CprK1(C11S), and CprK1(C200S) proteins (5.8 μg) that were heat denatured in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 5% β-mercaptoethanol (β-ME). CprK1(C11S) and CprK1(C200S) proteins each contain a C-terminal six-His tag, causing a slight difference in their mobilities compared to that of wild-type CprK1 on SDS-PAGE gels but leaving other properties of the proteins unaffected. (B) In vivo promoter probe assay using E. coli JM109(DE3) cells harboring plasmid pWUR166 with a DB3::lacLM promoter fusion and a pET24d plasmid derivative that overproduces either wild-type CprK1, CprK1(C11S), or CprK1(C200S) protein. Cells were grown either in the presence of 20 mM Cl-OHPA (solid bars) or in the absence of the effector (shaded bars).