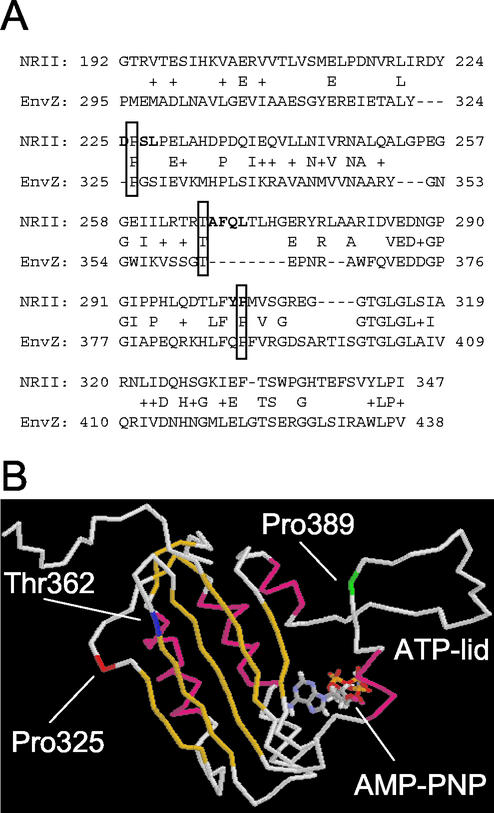
FIG. 8.
Structure of the kinase domain of EnvZ modeled to show the approximate positions of the mutations obtained in NRII. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of the kinase domains of NRII and EnvZ. The alignment was generated using a basic BLAST search of the E. coli genome with full-length NRII (accession number AAC76866) as the query (1). The residues shown in bold indicate the positions of the mutations obtained in the kinase domain of NRII. Shown boxed are conserved residues that were used as “anchor” points to represent positions of mutations obtained in NRII. Pro226 (NRII)/Pro325 (EnvZ) represents the cluster of mutations obtained at positions 225 to 228, Thr266 (NRII)/Thr362 (EnvZ) represents the deletion of residues 267 to 270, and Pro303 (NRII)/Pro389 (EnvZ) represents the cluster of mutations obtained at positions 302 to 303. (B) Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging structure of the kinase domain of EnvZ (52) shown as an alpha-carbon trace. Alpha-helices are shown in magenta, and beta-strands are shown in yellow. The AMP-PNP molecule is shown in stick representation with CPK coloring. The positions of Pro325 (representing the 225-to-228 cluster), Thr362 (representing the deletion), and Pro389 (representing the 302-to-303 cluster) are shown in red, blue, and green, respectively. The figure was generated using RasMol.