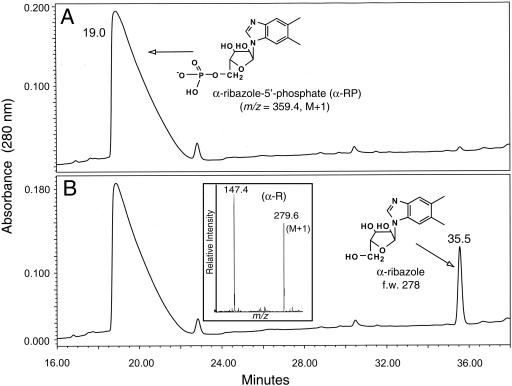
FIG. 3.
CobZ protein dephosphporylates α-RP. Shown are the high-pressure liquid chromatograms of CobZ reactions. A. Reaction mixture containing heat-inactivated CobZ enzyme; B. CobZ reaction. α-RP and α-ribazole eluted 19 and 35.5 min after injection, respectively. The inset in panel B shows the electrospray ionization mass spectrometry spectrum (positive ionization mode) of the reaction product. The signals with m/z values of 279.6 (M + 1) and 147.4 (M + 1) were consistent with the molecular masses of α-ribazole and DMB, respectively. Substrate and products of the CobZ reaction were filtered using a Spin X centrifuge tube filter (Corning) and analyzed by reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography as described previously (12, 26). Phosphatase activity was measured in reaction mixtures (100 μl) containing α-RP (40 nmol), in 30 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8) containing MgCl2 (9 mM) and KCl (0.1 M), and in homogeneous H10CobZ protein (5 μg [0.25 nmol]). Reaction mixtures were prepared on ice, transferred, and kept in a 37°C heater for 1 h and then heated to 80°C for 10 min to terminate the reaction. Heat-inactivated H10CobZ protein was used as a negative control, and shrimp alkaline phosphatase (Promega) was used as a positive control. High-performance liquid chromatography-purified product of the CobZ reaction was dried under vacuum using a SpeedVac concentrator (Savant) prior to mass spectrometry analysis at the MS Facility at the University of Wisconsin-Madison Biotechnology Center. Mass spectra were obtained using a Perkin-Elmer Sciex API365 mass spectrometer. f.w., formula weight.