Abstract
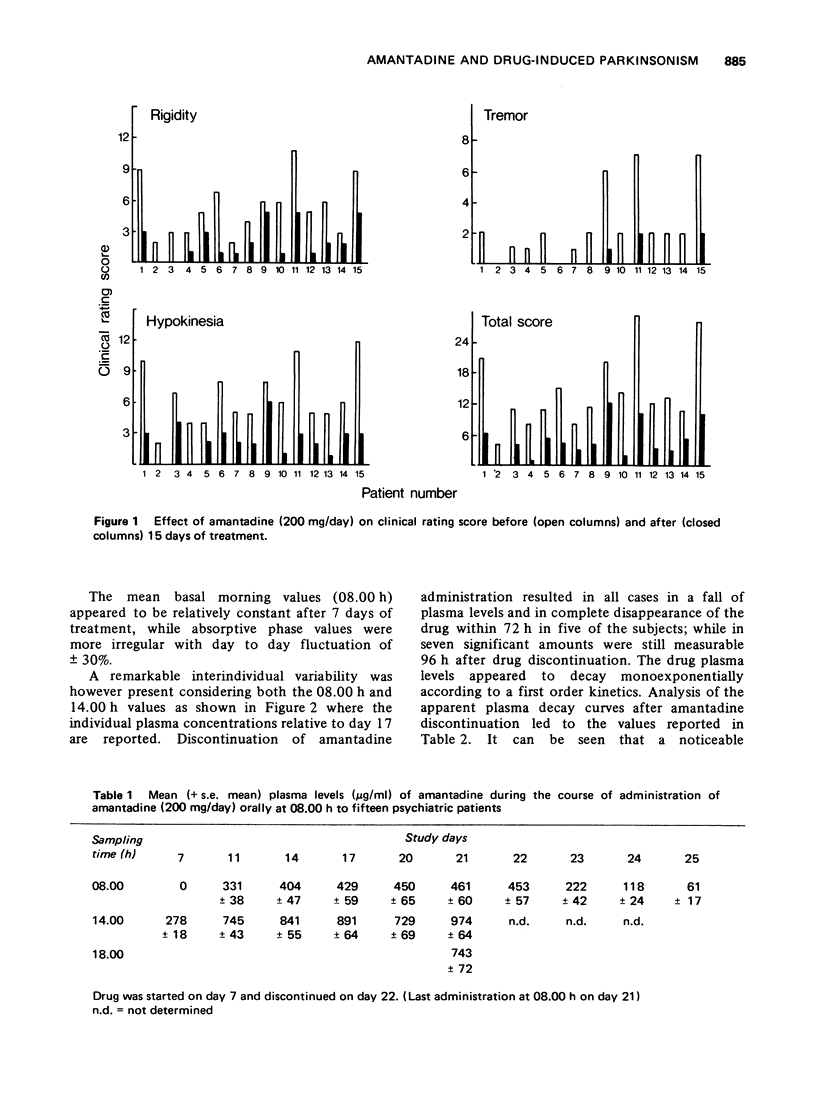
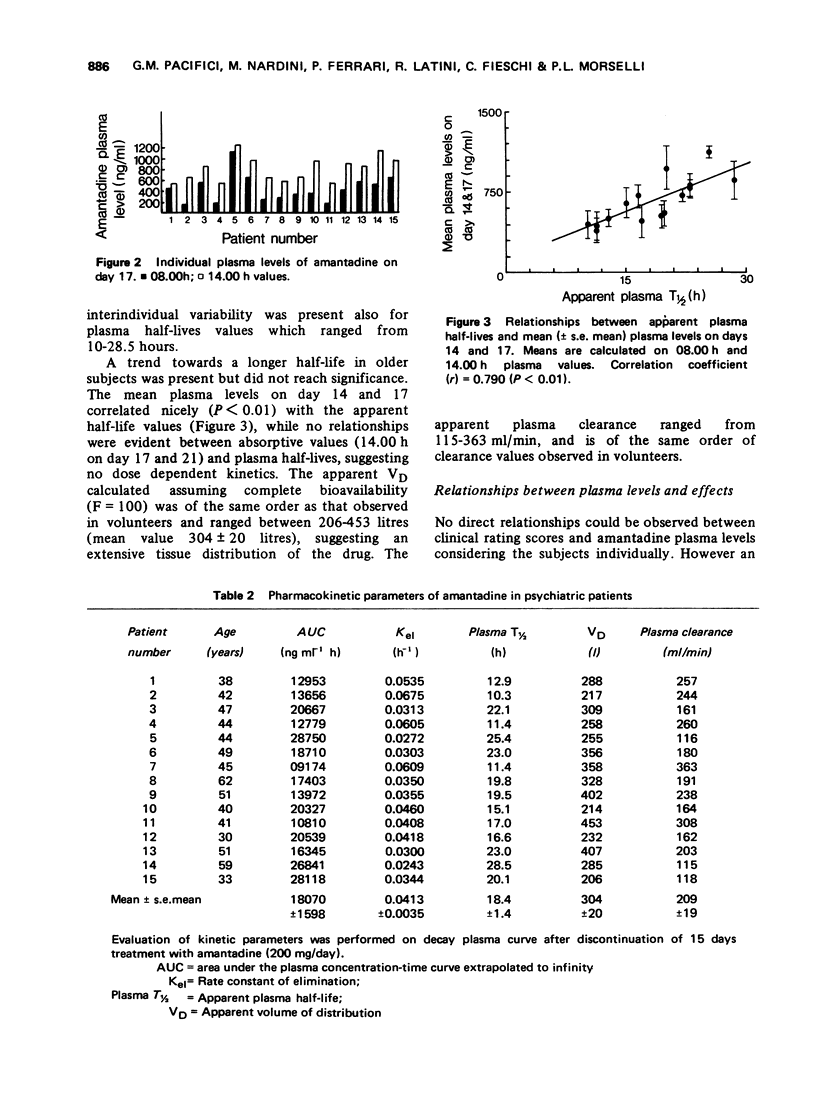
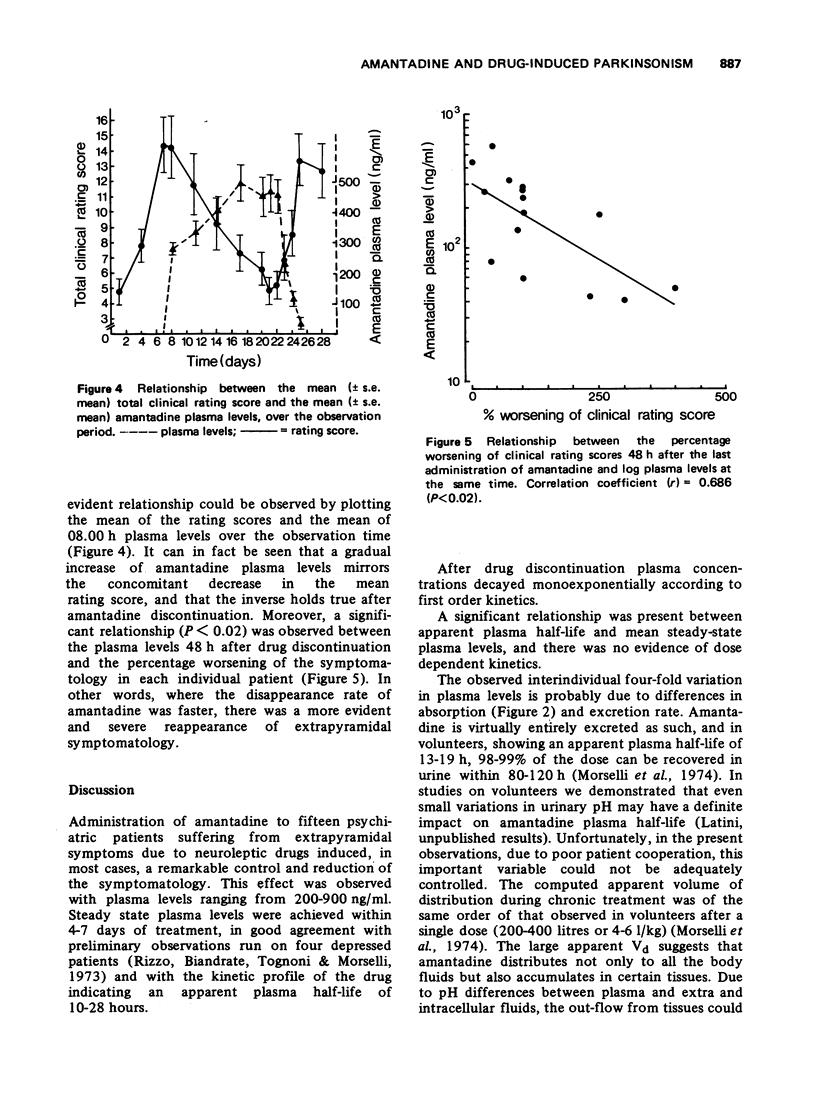
Amantadine, administered at a dose of 200 mg/day, antagonized the extapyramidal symptomatology induced by neuroleptic drugs in fifteen psychiatric patients. Steady-state levels were reached within 4-7 days of treatment. Individual plasma levels ranged from 200-900 ng/ml. Apparent plasma half-lives varied from 10-28.5 h with an apparent VD of 200-400 litres. A significant relationship was found between the plasma levels of amantadine and the effects on the extrapyramidal symptomatology. The data suggest a direct effect of amantadine on dopaminergic receptors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer R. B., McHenry J. T. Comparison of amantadine, placebo, and levodopa in Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1974 Aug;24(8):715–720. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.8.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biandrate P., Tognoni G., Belvedere G., Frigerio A., Rizzo M., Morselli P. L. A gas chromatographic method for the determination of amantadine in human plasma. J Chromatogr. 1972 Dec 6;74(1):31–34. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)94969-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown F., Redfern P. H. Proceedings: The effect of amantadine on the turnover of catecholamines in the rat brain. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1974 Dec;26 (Suppl):81P–82P. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1974.tb10106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanali A., Nardini M., Sorgona F. Azione della amantadina nelle sindromi extrapiramidali da neurolettici. Sist Nerv. 1970 Sep-Oct;22(5):273–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnebo L. O., Fuxe K., Goldstein M., Hamberger B., Ungerstedt U. Dopamine and noradrenaline releasing action of amantadine in the central and peripheral nervous system: a possible mode of action in Parkinson's disease. Eur J Pharmacol. 1971 Sep;16(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(71)90053-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieschi C., Nardini M., Casacchia M., Reitano M., Tedone M. E., Ferrari P., Robotti E. Terapia farmacologica della malattia di Parkinson con amantadina e levodopa. Sist Nerv. 1970 Mar-Jun;22(2):126–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieschi C., Nardini M., Casacchia M., Tedone M. E. Amantadine for Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 1970 May 2;1(7653):945–946. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieschi C., Nardini M., Casacchia M., Tedone M. E., Reitano M., Robotti E. Amantadine versus L-2 dopa and amatadine plus L-dopa. Lancet. 1970 Jul 18;2(7664):154–155. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92742-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter K. R., Stern G. M., Laurence D. R., Armitage P. Amantadine in parkinsonism. Lancet. 1970 May 30;1(7657):1127–1129. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter K. R., Stern G. M., Laurence D. R., Armitage P. Combined treatment of parkinsonism with L-dopa and amantadine. Lancet. 1970 Sep 12;2(7672):566–566. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91365-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. T., Abuzzahab F. S., Sr The antiparkinson properties of amantadine in drug-induced parkinsonism. J Clin Pharmacol New Drugs. 1971 May-Jun;11(3):211–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maj J., Sowińska H., Baran L. The effect of amantadine on motor activity and catalepsy in rats. Psychopharmacologia. 1972;24(2):296–307. doi: 10.1007/BF00403648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. C., Pearce L. A., Waterbury L. D. Amantadine for Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1971 Sep;21(9):958–962. doi: 10.1212/wnl.21.9.958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawdsley C., Williams I. R., Pullar I. A., Davidson D. L., Kinloch N. E. Treatment of parkinsonism by amantadine and levodopa. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1972 Jul-Aug;13(4):575–583. doi: 10.1002/cpt1972134575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick E. M., Schmitt P. P. A controlled study of the clinical effects of amantadine hydrochloride (Symmetrel). Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1973 Aug;15(8):552–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardini M., Fanali A., Sorgonà F., Vergnano M., Fieschi G. Studio clinico dell'amantadina nella sindrome extrapiramidale da neurolettici. Minerva Med. 1971 Oct 31;62(82):4020–4023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papeschi R. Amantadine may stimulate dopamine and noradrenaline receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1974 Jan;13(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(74)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scatton B., Cheramy A., Besson M. J., Glowinski J. Increased synthesis and release of dopamine in the striatum of the rat after amantadine treatment. Eur J Pharmacol. 1970;13(1):131–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(70)90194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab R. S., England A. C., Jr, Poskanzer D. C., Young R. R. Amantadine in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. JAMA. 1969 May 19;208(7):1168–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab R. S., Poskanzer D. C., England A. C., Jr, Young R. R. Amantadine in Parkinson's disease. Review of more than two years' experience. JAMA. 1972 Nov 13;222(7):792–795. doi: 10.1001/jama.222.7.792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Bailey E. V. Responses of central neurones to amantadine: comparison with dopamine and amphetamine. Brain Res. 1975 Feb 21;85(1):126–129. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)91017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromberg U., Svensson T. H., Waldeck B. On the mode of action of amantadine. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1970 Dec;22(12):959–962. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1970.tb08487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


