Abstract
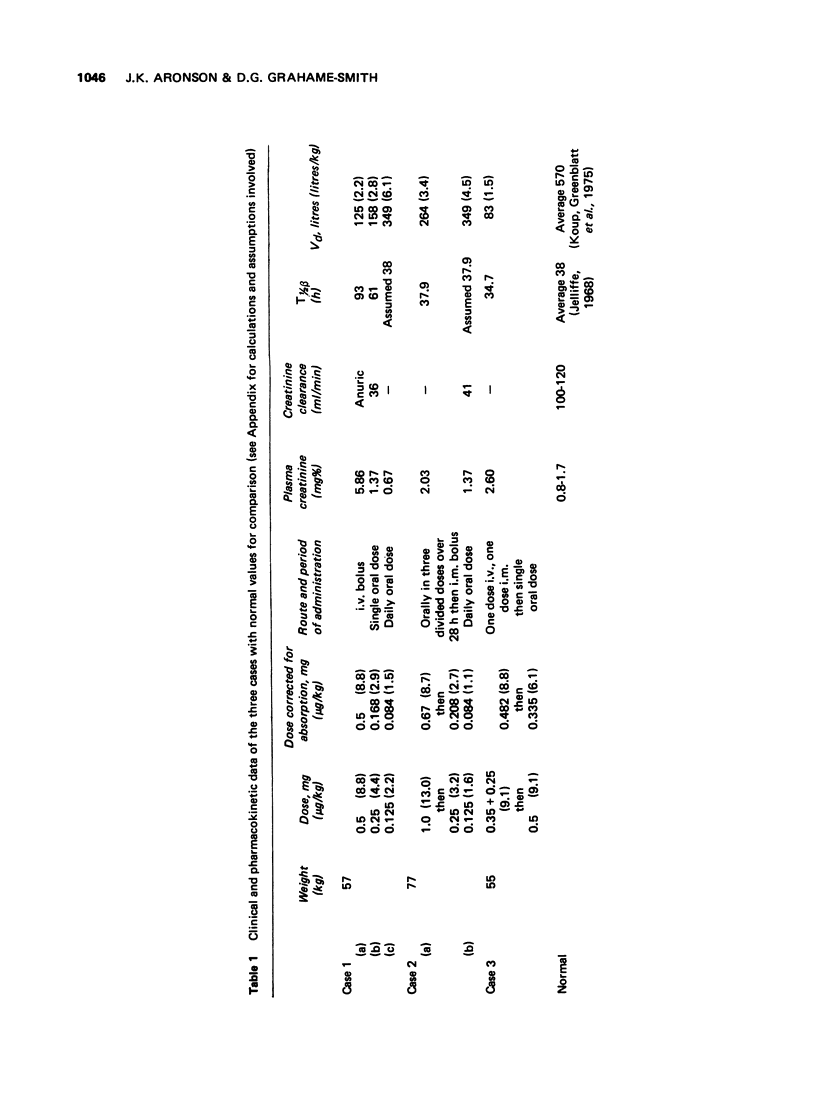
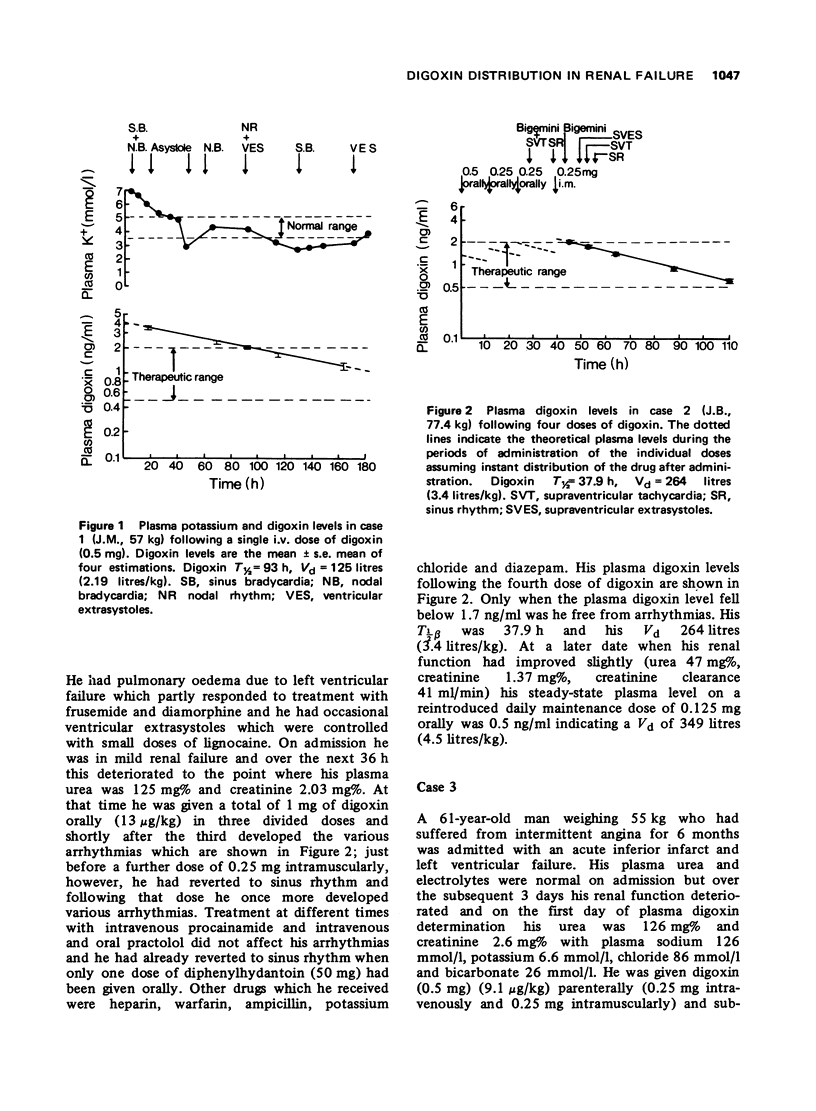
1 Three cases are described in which renal failure was accompanied by a lowered apparent volume of distribution of digoxin. In two cases this resulted in frank digoxin toxicity and in one equivocal toxicity. In all three cases digoxin plasma levels were greater than 2 ng/ml.
2 The possible causes of the abnormal distribution of digoxin in renal failure are discussed.
3 Recommendations are outlined for the use of digoxin in patients with renal failure aimed at circumventing the problem raised by a lowered apparent volume of distribution of the drug.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beller G. A., Smith T. W., Abelmann W. H., Haber E., Hood W. B., Jr Digitalis intoxication. A prospective clinical study with serum level correlations. N Engl J Med. 1971 May 6;284(18):989–997. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197105062841801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. H., Balfe J. W., Welt L. G. Induction of a ouabain-sensitive ATPase defect by uremic plasma. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1968;81:213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. H. Decreased ouabain-sensitive adenosine triphosphatase activity in the erythrocyte membrame of patients with chronic renal disease. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Dec;45(6):775–784. doi: 10.1042/cs0450775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coltart D. J., Güllner H. G., Billingham M., Goldman R. H., Stinson E. B., Kalman S. M., Harrison D. C. Physiological distribution of digoxin in human heart. Br Med J. 1974 Dec 28;4(5947):733–736. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5947.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOHERTY J. E., PERKINS W. H., WILSON M. C. STUDIES WITH TRITIATED DIGOXIN IN RENAL FAILURE. Am J Med. 1964 Oct;37:536–544. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty J. E., Flanigan W. J., Patterson R. M., Dalrymple G. V. The excretion of tritiated digoxin in normal human volunteers before and after unilateral nephrectomy. Circulation. 1969 Oct;40(4):555–561. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.40.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty J. E., Kane J. J. Clinical pharmacology of digitalis glycosides. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:159–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. H., Coltart D. J., Friedman J. P., Nola G. T., Berke D. K., Schweizer E., Harrison D. C. The inotropic effects of digoxin in hyperkalemia. Relation to (Na+,K+)-ATPase inhibition in the intact animal. Circulation. 1973 Oct;48(4):830–838. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.48.4.830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelliffe R. W. An improved method of digoxin therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Oct;69(4):703–717. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-69-4-703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jusko W. J., Weintraub M. Myocardial distribution of digoxin and renal function. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Sep;16(3):449–454. doi: 10.1002/cpt1974163part1449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koup J. R., Greenblatt D. J., Jusko W. J., Smith T. W., Koch-Weser J. Pharmacokinetics of digoxin in normal subjects after intravenous bolus and infusion doses. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1975 Jun;3(3):181–192. doi: 10.1007/BF01067907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koup J. R., Jusko W. J., Elwood C. M., Kohli R. K. Digoxin pharmacokinetics: role of renal failure in dosage regimen design. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Jul;18(1):9–21. doi: 10.1002/cpt19751819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS F. I., KAPADIA G. J., KAPADIA G. G. THE METABOLISM OF DIGOXIN IN NORMAL SUBJECTS. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Aug;145:203–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus F. I., Peterson A., Salel A., Scully J., Kapadia G. G. The metabolism of tritiated digoxin in renal insufficiency in dogs and man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Jun;152(3):372–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuning R. H., Sams R. A., Notari R. E. Role of pharmacokinetics in drug dosage adjustment. I. Pharmacologic effect kinetics and apparent volume of distribution of digoxin. J Clin Pharmacol New Drugs. 1973 Apr;13(4):127–141. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1973.tb00074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. G. Loading and maintenance doses of digoxin in patients with normal renal function and those with severely impaired renal function. J Clin Pharmacol. 1974 Jul;14(7):329–338. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1974.tb01408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. G., Northam J. I., Alway C. D., Carpenter O. S. Blood levels of drug at the equilibrium state after multiple dosing. Nature. 1965 Sep 18;207(5003):1301–1302. doi: 10.1038/2071301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. G., Northam J. I. Estimation of volume of distribution and half-life of a compound after rapid intravenous injection. J Pharm Sci. 1967 Apr;56(4):529–531. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600560424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welt L. G. Membrane transport defect: the sick cell. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1967;80:217–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. R. Pharmacokinetics of drug disposition: hemodynamic considerations. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1975;15:11–27. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.15.040175.000303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


