Abstract
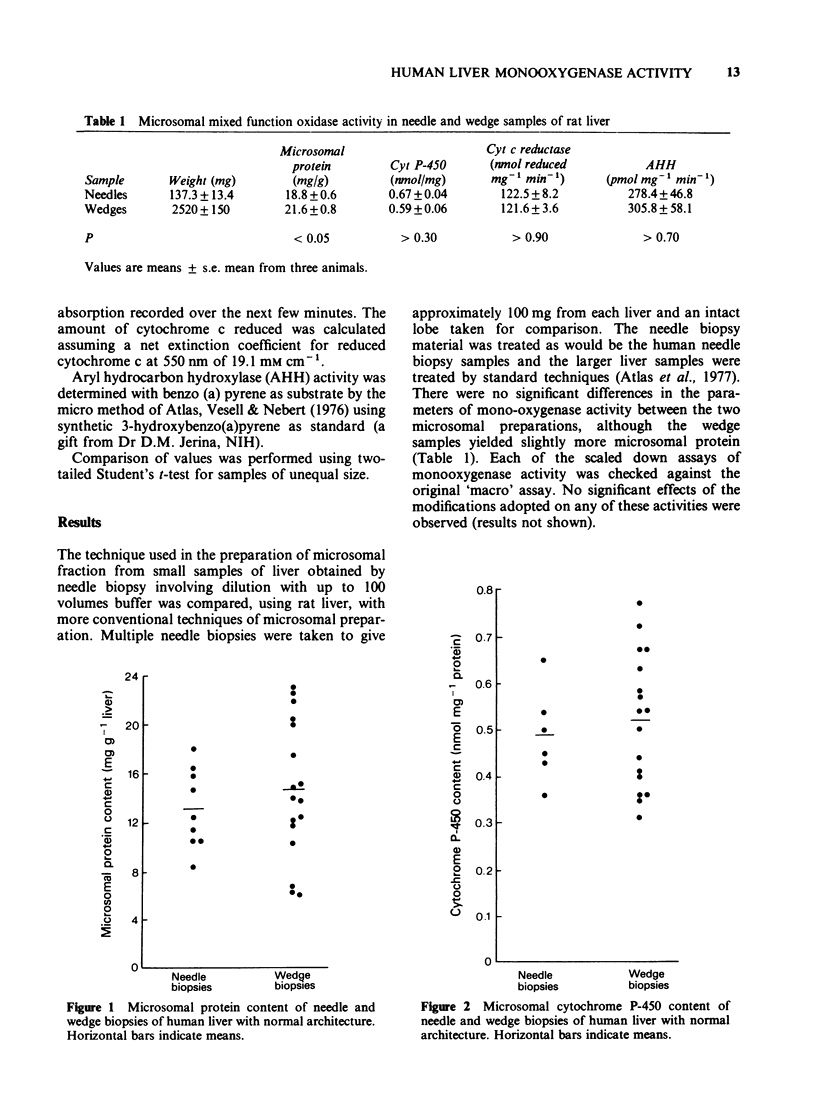
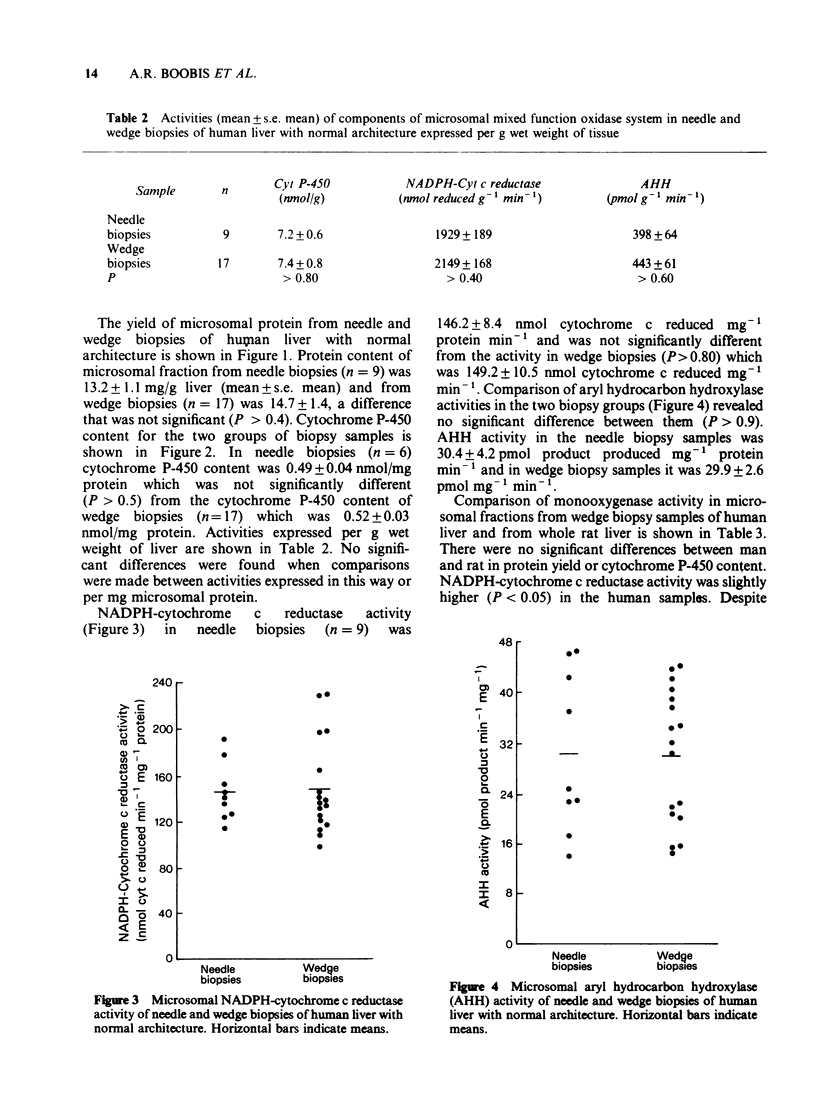
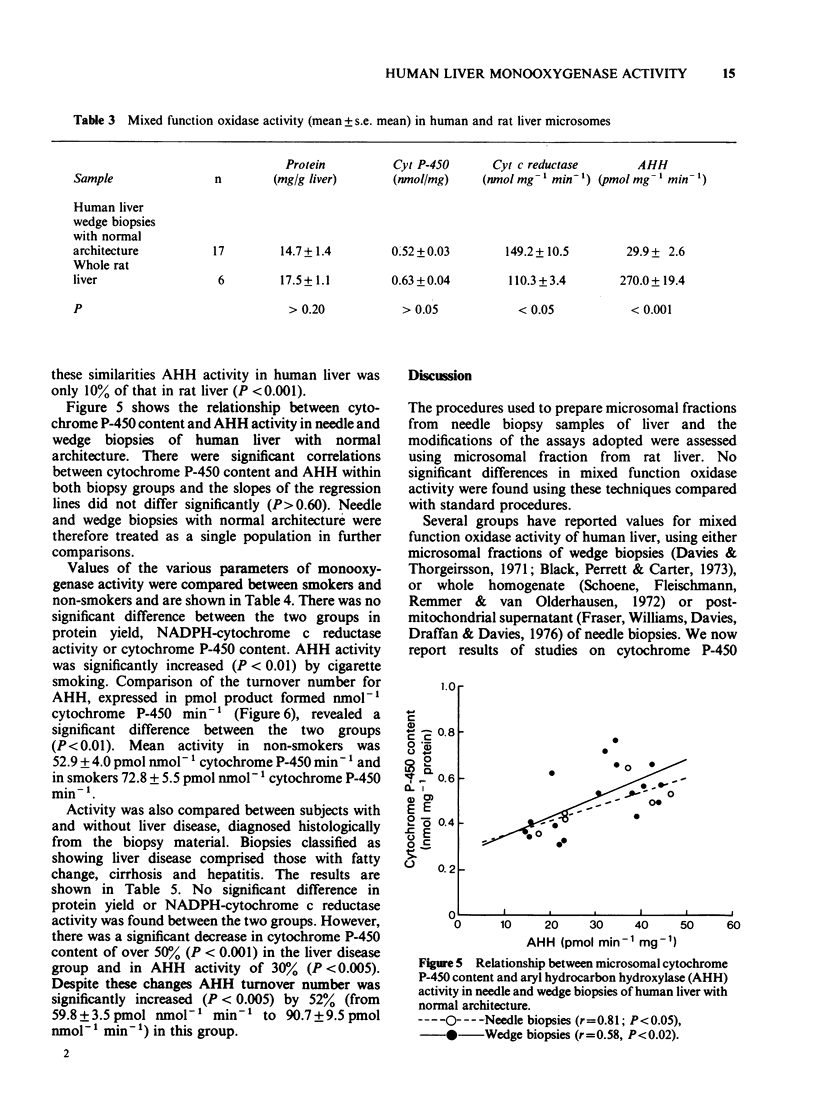
1 Methods are described for the determination of mixed function oxidase activity in microsomal fractions from percutaneous needle biopsies of human liver. 2 Activities of needle biopsy samples were comparable with those of wedge biopsy sample obtained at laparotomy from different subjects. 3 Although cytochrome P-450 content of liver from rat and man was similar, human AHH activity was only 10% of that in the rat. 4 In biopsies with preserved hepatic architecture, AHH activity and cytochrome P-450 content showed a significant positive correlation. 5 Cigarette smoking significantly increased both AHH activity and turnover number, but not cytochrome P-450 content, of biopsies with normal architecture. 6 The presence of liver disease caused a significant decrease in AHH activity and cytochrome P-450 content.
Full text
PDF

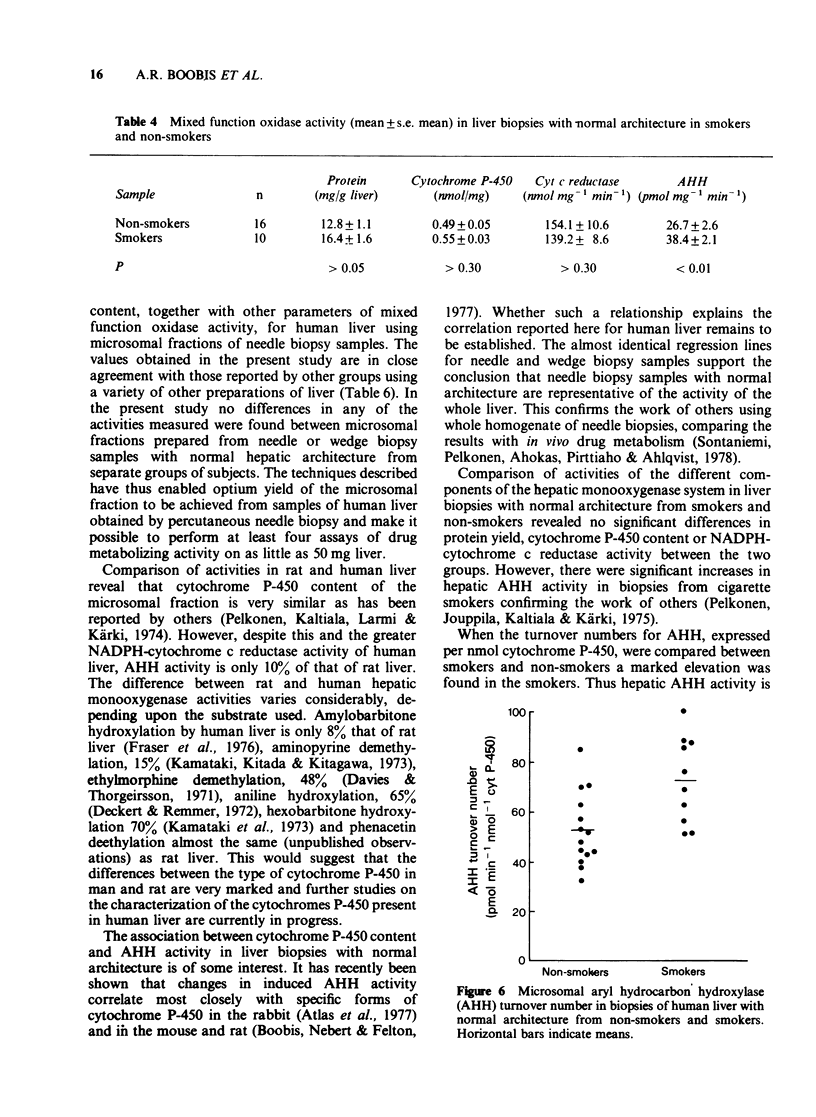


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann E. Entalkylierung von Athylmorphin und p-C-hydroxylierung von Anilin in Lebermikrosomen von Menschen und von Männlichen und Weiblichen Ratten. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Aug 15;21(16):2169–2180. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann E., Heinrich I. Die Aktivität der N- und O-Demethylase in der Leber des Menschen. Biochem Pharmacol. 1970 Feb;19(2):327–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(70)90190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvares A. P., Schilling G., Levin W., Kuntzman R., Brand L., Mark L. C. Cytochromes P-450 and b5 in human liver microsomes. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1969 Sep-Oct;10(5):655–659. doi: 10.1002/cpt1969105655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas S. A., Boobis A. R., Felton J. S., Thorgeirsson S. S., Nebert D. W. Ontogenetic expression of polycyclic aromatic compound-inducible monooxygenase activities and forms of cytochrome P-450 in rabbit. Evidence for temporal control and organ specificity of two genetic regulatory systems. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4712–4721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas S. A., Vesell E. S., Nebert D. W. Genetic control of interindividual variations in the inducibility of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase in cultured human lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 1976 Dec;36(12):4619–4630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODIE B. B., AXELROD J., COOPER J. R., GAUDETTE L., LA DU B. N., MITOMA C., UDENFRIEND S. Detoxication of drugs and other foreign compounds by liver microsomes. Science. 1955 Apr 22;121(3147):603–604. doi: 10.1126/science.121.3147.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black M., Perrett R. D., Carter A. E. Hepatic bilirubin UDP-glucuronyl transferase activity and cytochrome P450 content in a surgical population, and the effects of preoperative drug therapy. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 May;81(5):704–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boobis A. R., Nebert D. W., Felton J. S. Comparison of beta-naphthoflavone and 3-methylcholanthrene as inducers of hepatic cytochrome(s) P-448 and aryl hydrocarbon (benzo[a]pyrene) hydroxylase activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;13(2):259–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai K., Gaylor J. L. Existence and separation of three forms of cytochrome P-450 from rat liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):4947–4955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby F. J., Grundy R. K. The metabolism of (ureyl-14C)tolbutamide in vitro and in vivo in man. Life Sci. 1973 Jul 16;13(2):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(73)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. S., Thorgeirsson S. S., Breckenridge A., Orme M. Interindividual differences in rates of drug oxidation in man. Drug Metab Dispos. 1973 Jan-Feb;1(1):411–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. S., Thorgeirsson S. S. Mechanism of hepatic drug oxidation and its relationship to individual differences in rates of oxidation in man. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jul 6;179:411–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb46918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckert F. W., Remmer H. K. In vitro inhibition of rat and human liver microsomal enzymes by 4-hydroxycoumarin anticoagulants and related compounds. Chem Biol Interact. 1972 Sep;5(4):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(72)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dybing E., Nelson S. D., Mitchell J. R., Sasame H. A., Gillette J. R. Oxidation of alpha-methyldopa and other catechols by cytochrome P-450-generated superoxide anion: possible mechanism of methyldopa hepatitis. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;12(6):911–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover P. L., Sims P. Enzyme-catalysed reactions of polycyclic hydrocarbons with deoxyribonucleic acid and protein in vitro. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(1):159–160. doi: 10.1042/bj1100159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartoma T. R., Sotaniemi E. A., Pelkonen O., Ahlqvist J. Serum zinc and serum copper and indices of drug metabolism in alcoholics. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Oct 14;12(2):147–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00645136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen D. A., Coon M. J. Induction of multiple forms of mouse liver cytochrome P-450. Evidence for genetically controlled de novo protein synthesis in response to treatment with beta-naphthoflavone or phenobarbital. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1817–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jollow D. J., Mitchell J. R., Potter W. Z., Davis D. C., Gillette J. R., Brodie B. B. Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis. II. Role of covalent binding in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Oct;187(1):195–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamataki T., Kitada M., Kitagawa H. Some observations on the microsomal electron transport system and activities of drug oxidizing enzymes in human liver. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1973 Jan;21(1):8–11. doi: 10.1248/cpb.21.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitulnik J., Popper P. J., Conney A. H. Comparative metabolism of benzo[a]pyrene and drugs in human liver. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Feb;21(2):166–176. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977212166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. Y., Levin W., West S. B., Jacobson M., Ryan D., Kuntzman R., Conney A. H. Reconstituted liver microsomal enzyme system that hydroxylates drugs, other foreign compounds, and endogenous substrates. VI. Different substrate specificities of the cytochrome P450 fractions from control and phenobarbital-treated rats. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):456–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz F., Failinger C., 3rd, Blake D. A. Phenytoin teratogenesis: correlation between embryopathic effect and covalent binding of putative arene oxide metabolite in gestational tissue. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Oct;203(1):231–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Levitt R. C., Orlando M. M., Felton J. S. Effects of environmental chemicals on the genetic regulation of microsomal enzyme systems. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Nov;22(5 Pt 2):640–658. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977225part2640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E. B., Raj P. P., Belfi K. J., Masters B. S. Oxidative drug metabolism in human liver microsomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Sep;178(3):580–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson S. D., Mitchell J. R., Timbrell J. A., Snodgrass W. R., Corcoran G. B., 3rd Isoniazid and iproniazid: activation of metabolites to toxic intermediates in man and rat. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):901–903. doi: 10.1126/science.7838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. I. EVIDENCE FOR ITS HEMOPROTEIN NATURE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2370–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelkonen O., Kaltiala E. H., Kärki N. T., Jalonen K., Pyörälä K. Properties of benzpyrene hydroxylase from human liver and comparison with the rat, rabbit and guinea-pig enzymes. Xenobiotica. 1975 Aug;5(8):501–509. doi: 10.3109/00498257509056120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelkonen O., Kaltiala E. H., Larmi T. K., Kärki N. T. Comparison of activities of drug-metabolizing enzymes in human fetal and adult livers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 Sep-Oct;14(5):840–846. doi: 10.1002/cpt1973145840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelkonen O., Kaltiala E. H., Larmi T. K., Kärki N. T. Cytochrome P-450-linked monooxygenase system and drug-induced spectral interactions in human liver microsomes. Chem Biol Interact. 1974 Sep;9(3):205–216. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(74)80005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj P. P., Nelson E. B., Estabrook R. W. Studies on drug metabolism in human liver. Chem Biol Interact. 1971 Aug;3(4):303–304. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(71)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato N., Kamada T., Abe H., Suematsu T., Kawano S., Hayashi N., Matsumura T., Hagihara B. Simultaneous measurement of mitochondrial and microsomal cytochrome levels in human liver biopsy. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Oct 15;80(2):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoene B., Fleischmann R. A., Remmer H., von Oldershausen H. F. Determination of drug metabolizing enzymes in needle biopsies of human liver. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1972 Mar;4(2):65–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00562499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotaniemi E. A., Pelkonen R. O., Ahokas J., Pirttiaho H. I., Ahlqvist J. Drug metabolism in epileptics: in vivo and in vitro correlations. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;5(1):71–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01600.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. E., Lu A. Y., Ryan D., West S. B., Kawalek J., Levin W. Immunochemical evidence for six forms of rat liver cytochrome P450 obtained using antibodies against purified rat liver cytochromes P450 and P448. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Sep;12(5):746–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich V., Weber P., Wollenberg P. Tetrahydrofurane - an inhibitor for ethanol-induced liver microsomal cytochrome P450. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 2;64(3):808–813. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebel F. J., Selkirk J. K., Gelboin H. V., Haugen D. A., van der Hoeven T. A., Coon M. J. Position-specific oxygenation of benzo(a)pyrene by different forms of purified cytochrome P-450 from rabbit liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3917–3920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bahr C., Hedlund I., Karlén B., Bäckström D., Grasdalen H. Evidence for two catalytically different binding sites of liver microsomal cytochrome P-450: importance for species and sex differences in oxidation pattern of lidocaine. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1977 Jul;41(1):39–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1977.tb02121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


