Abstract
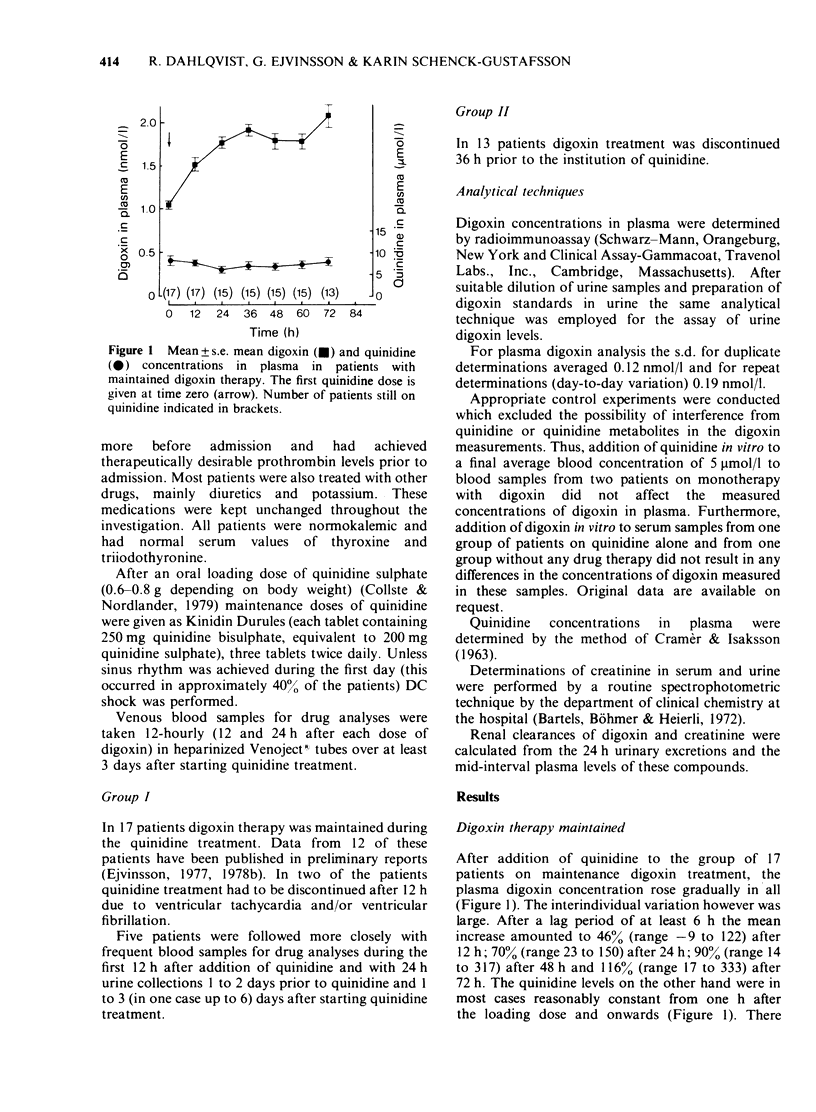
1 Thirty patients on maintenance digoxin therapy and admitted for cardioversion of atrial fibrillation were closely monitored with regard to plasma levels of digoxin and quinidine. 2 Seventeen of these patients were kept on maintenance digoxin therapy. After an initial lag period of 6 to 18 h after the addition of quinidine their digoxin levels started to increase and had increased by between 20 and 330% after 3 days on quinidine. Side-effects attributed to the raised digoxin concentration occurred in 6 of these patients. 3 As studied in 5 of these 17 patients the renal clearance of digoxin decreased markedly when quinidine was added to the therapy. There was also a slight but significant reduction in creatinine clearance (n = 4). 4 In 13 patients digoxin was discontinued 36 h prior to the first quinidine dose. Also in these patients digoxin plasma levels increased significantly. 5 It is concluded that quinidine causes an unpredictably large increase in plasma digoxin and that this effect is probably at least initially to a large part due to a redistribution of digoxin in the body. The relative contributions of re-distribution and impaired renal clearance of digoxin to the increase in digoxin steady-state levels are presently unknown. 6 It is recommended that close monitoring of digoxin concentration and appropriate reduction of the maintenance dose is undertaken when quinidine is to be given to patients on digitalis therapy.
Full text
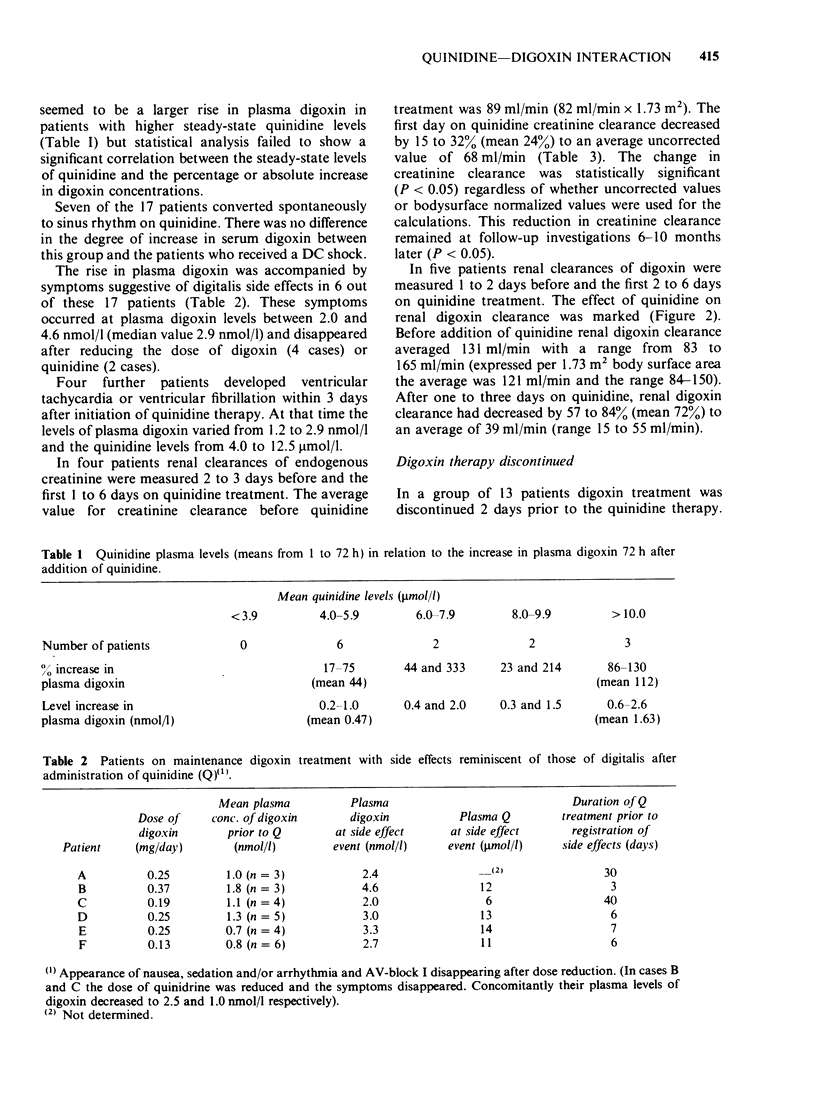
PDF
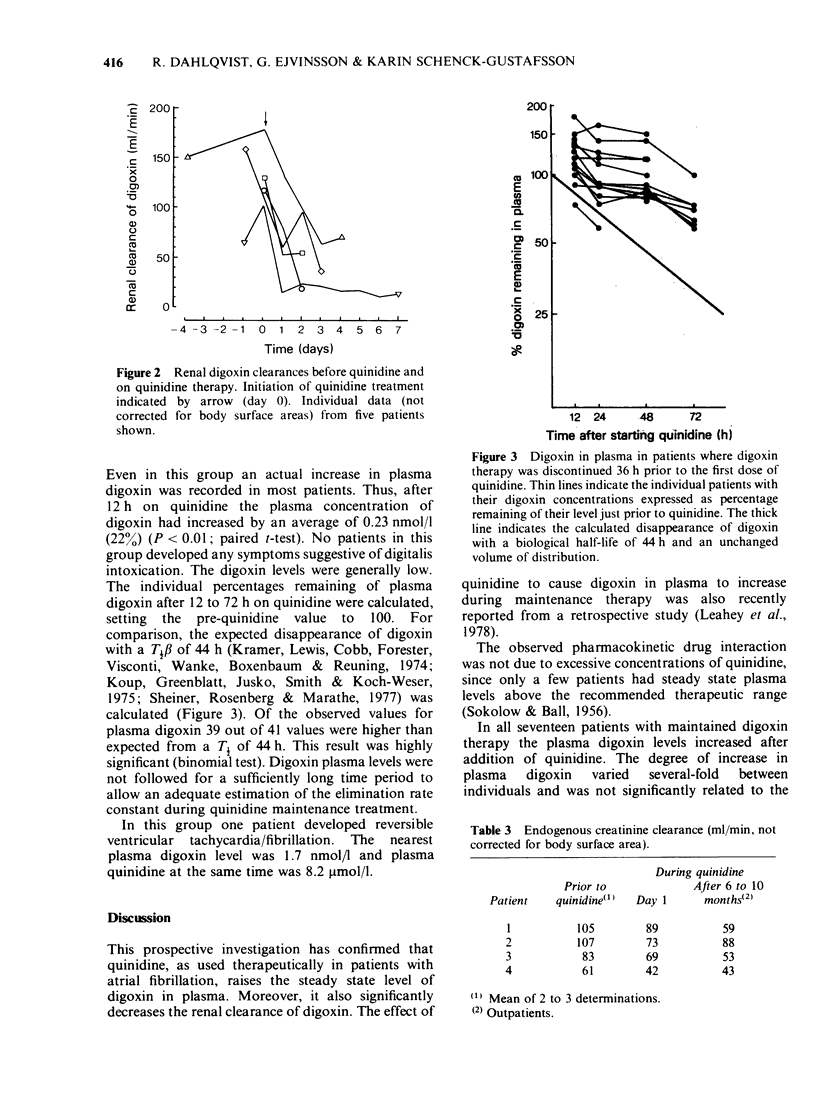


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALL R. E., SOKOLOW M. Factors influencing conversion of chronic atrial fibrillation with special reference to serum quinidine concentration. Circulation. 1956 Oct;14(4 Pt 1):568–583. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.14.4.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartels H., Böhmer M., Heierli C. Serum Kreatinibestimmung ohne Enteiweissen. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Mar;37:193–197. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90432-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerkelund C., Skåland K. Kinidin som årsak til paroxystisk ventrikkelflimmer. Nord Med. 1967 Jan 19;77(3):76–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAMER G., ISAKSSON B. QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF QUINIDINE IN PLASMA. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1963;15:553–556. doi: 10.1080/00365516309079786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellanos A., Jr, Lemberg L., Johnson D., Gilmore H., 3rd Countershock exposed quinidine syncope. Am J Med Sci. 1965 Sep;250(3):254–260. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196509000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collste P., Nordlander R. Quinidine dosage, with special reference to an oral loading dose schedule. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Mar;7(3):293–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb00935.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOHERTY J. E., PERKINS W. H. Studies with tritiated digoxin in human subjects after intravenous administration. Am Heart J. 1962 Apr;63:528–536. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(62)90310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derweduwen H., Enderle J., De Geest H., Polis O., Vancrombreucq J. C., Joossens J. V. Direct-current shock in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. A clinical study. Acta Cardiol. 1969;24(3):205–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejvinsson G. Effect of quinidine on plasma concentrations of digoxin. Br Med J. 1978 Feb 4;1(6108):279–280. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6108.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERT R., CUDDY R. P. DIGITALIS INTOXICATION FOLLOWING CONVERSION TO SINUS RHYTHM. Circulation. 1965 Jul;32:58–64. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.32.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager W. D., Fenster P., Mayersohn M., Perrier D., Graves P., Marcus F. I., Goldman S. Digoxin-quinidine interaction Pharmacokinetic evaluation. N Engl J Med. 1979 May 31;300(22):1238–1241. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197905313002202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooymans P. M., Merkus F. W. Effect of quinidine on plasma concentration of digoxin. Br Med J. 1978 Oct 7;2(6143):1022–1022. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6143.1022-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelliffe R. W. An improved method of digoxin therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Oct;69(4):703–717. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-69-4-703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W. G., Lewis R. P., Cobb T. C., Forester W. F., Jr, Visconti J. A., Wanke L. A., Boxenbaum H. G., Reuning R. H. Pharmacokinetics of digoxin: comparison of a two- and a three-compartment model in man. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1974 Aug;2(4):299–312. doi: 10.1007/BF01061404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahey E. B., Jr, Reiffel J. A., Drusin R. E., Heissenbuttel R. H., Lovejoy W. P., Bigger J. T., Jr Interaction between quinidine and digoxin. JAMA. 1978 Aug 11;240(6):533–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS F. I., KAPADIA G. J., KAPADIA G. G. THE METABOLISM OF DIGOXIN IN NORMAL SUBJECTS. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Aug;145:203–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiner L. B., Rosenberg B., Marathe V. V. Estimation of population characteristics of pharmacokinetic parameters from routine clinical data. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1977 Oct;5(5):445–479. doi: 10.1007/BF01061728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldorff S., Andersen J. D., Heebøll-Nielsen N., Nielsen O. G., Moltke E., Sørensen U., Steiness E. Spironolactone-induced changes in digoxin kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Aug;24(2):162–167. doi: 10.1002/cpt1978242162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


