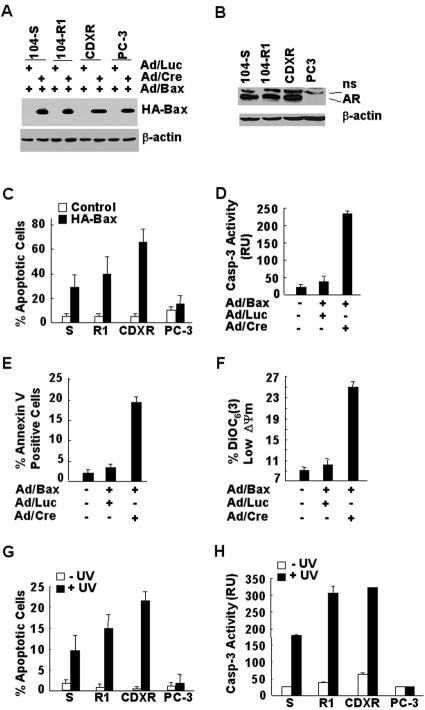
FIG. 1.
Bax and UV selectively induce apoptosis in AR-positive, but not in AR-negative prostate cancer cells. (A) Prostate cancer cell lines were infected with adenoviral vector encoding HA-Bax (Ad/Bax), Cre (Ad/Cre), or luciferase (Ad/Luc) (multiplicity of infection = 100, 24 h), as indicated. Expression of HA-Bax was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibody. (B) Expression levels of AR in various prostate cancer cell lines in panel A were examined by immunoblotting with anti-AR antibody (AN21). (C) The viability of the infected cells in panel A was measured by MTS assays. S, 104-S; R1, 104-R1. (D, E, and F) Apoptotic cell death of the infected 104-R1 cells in panel A was characterized by caspase activity assays with the fluorogenic caspase-3 substrate DEVD-AFC (D), by detecting apoptotic membrane alteration with FITC-annexin V staining (E), and by measuring the mitochondrial membrane potential changes (F), as indicated. (G and H) The same panel of cells in panel A was treated with or without UV radiation (10 mJ/cm2) for 16 h. Apoptotic cells were detected and quantitated by nuclear staining with Hoechst (H33258) (G) or by caspase assays using the fluorogenic substrate DEVD-AFC (H). S, 104-S; R1, 104-R1.