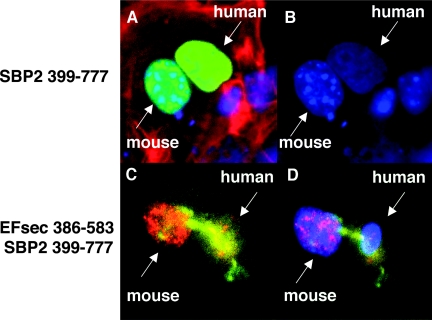
FIG. 4.
Nuclear colocalization and nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of SBP2 and EFsec. SBP2 minimal functional domain undergoes nucleocytoplasmic shuttling, as visualized in a heterokaryon assay using SBP 399-777-V5 transiently expressed in human MSTO-211H cells, followed by fusion with mouse NIH 3T3 cells. (A) V5 antibody staining in nuclei from both cell lines (green) merged with DAPI staining and filamentous actin localization with rhodamine-phalloidin (red). (B) DAPI staining used to distinguish human (diffuse) from mouse (punctuate) nuclei. EFsec 386-583 shuttles in the presence of SBP2 399-777. (C) Heterokaryon assay of EFsec 386-583 stained with anti-FLAG/1:500 followed by anti-rabbit antibody-Alexa Fluor 546 (red) and SBP2 399-777 stained with 1:200 anti-v5/1:500 followed by anti-mouse antibody-Alexa Fluor 488 (green) expressed in human MSTO-211H cells followed by fusion with mouse NIH-3T3 cells. (D) Blue fluorescence represents cell nucleus stained with DAPI. Yellow areas indicate the colocalization of green and red fluorescence, pink areas indicate the colocalization of blue and red fluorescence, and cyan areas indicate colocalization of blue and green fluorescence.