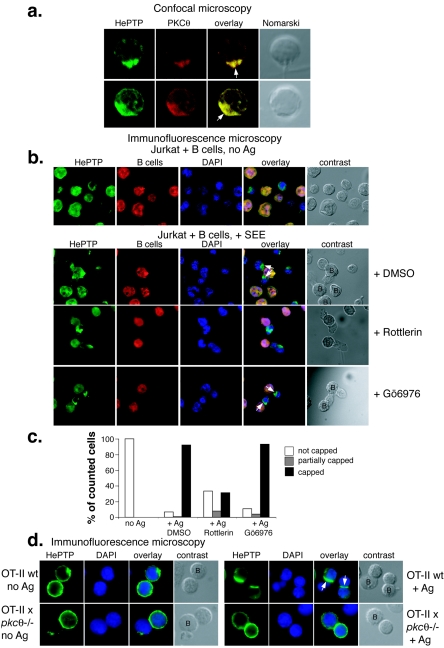
FIG. 3.
PKC θ is required for HePTP translocation to the immune synapse. (a) Confocal microscopy of CD8+ antigen-specific, TCR-transgenic OT-I T cells in contact with APCs for 20 min and stained for HePTP (green) and PKC θ (red). (b) Immunofluorescence microscopy of Jurkat T cells in contact with Raji B cells without (top row) or with (all other rows) staphylococcal enterotoxin E and stained for HePTP (green), B cells (red), and DNA (blue). The centers of the contacts between the T cell and the APC are indicated with arrows; B cells are labeled “B” in contrast panels. (c) Quantitation of formed immune synapses in numerous fields of view. (d) Immunofluorescence microscopy of CD4+ antigen-specific, TCR-transgenic OT-II T cells in contact with APCs in the absence (left panels) or presence (right panels) of OVA peptide and stained for HePTP (green) and DNA (blue). The upper panels show control OT-II T cells; the lower panels show T cells from OT-II × pkcθ−/− mice, as indicated. B cells are labeled “B” in contrast panels. wt, wild type; DAPI, 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide.