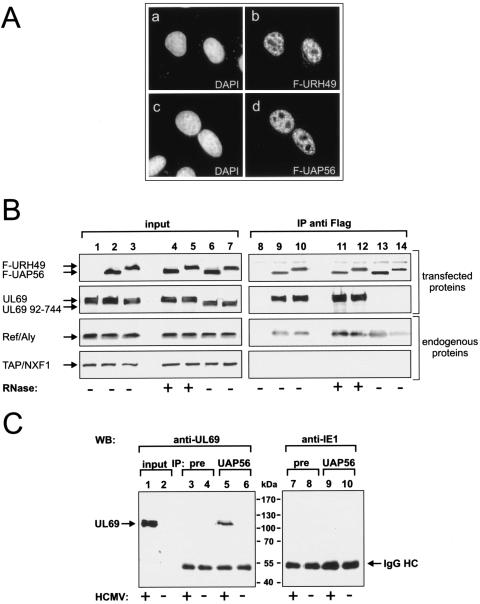
FIG. 4.
pUL69 is associated with nuclear UAP56- or URH49-containing complexes. (A) URH49 is mainly localized in the nucleoplasm of HeLa cells and shows a pattern similar to that observed for UAP56. FLAG-URH49 (a and b)- or FLAG-UAP56 (c and d)-expressing plasmids were transfected into HeLa cells which were subsequently immunostained using an anti-FLAG antibody. DAPI, 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (B) pUL69 is associated with UAP56 or URH49 and REF. HEK 293T cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding wt UL69 (lanes 1 to 5 and 8 to 12) or an N-terminal UL69 deletion mutant (UL69 92-744, lanes 6 and 7 and lanes 13 and 14) and FLAG-tagged proteins UAP56 (lanes 2, 4, 6, 9, 11, and 13) or URH49 (lanes 3, 5, 7, 10, 12, and 14). The amount of protein in the input was analyzed by Western blotting (input, lanes 1 to 7). Immunoprecipitation was performed using anti-FLAG antibody M2 (IP anti-FLAG, lanes 8 to 14). Coimmunoprecipitated proteins were visualized by Western blotting using either anti-FLAG, anti-UL69, anti-REF, or anti-TAP antibodies to detect the indicated proteins. For RNase treatment RNase A was added to the indicated extracts as described in Materials and Methods. (C) pUL69 forms a complex with UAP56 in HCMV-infected cells. HFF cells were mock infected (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10) or infected with HCMV AD169 (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9), and immunoprecipitation was performed using a polyclonal anti-UAP56 antibody (lanes 5, 6, 9, and 10) or a nonspecific preimmune serum (lanes 3, 4, 7, and 8). The amount of UL69 protein in the input (input; lanes 1 and 2) and the coimmunoprecipitated proteins (IP; lanes 3 to 10) were visualized by Western blotting. Lanes 1 to 6, Western blotting was performed with anti-UL69 monoclonal antibody; lanes 7 to 10, Western blotting was performed with anti-IE1 monoclonal antibody. IgG HC, immunoglobulin G heavy chain.