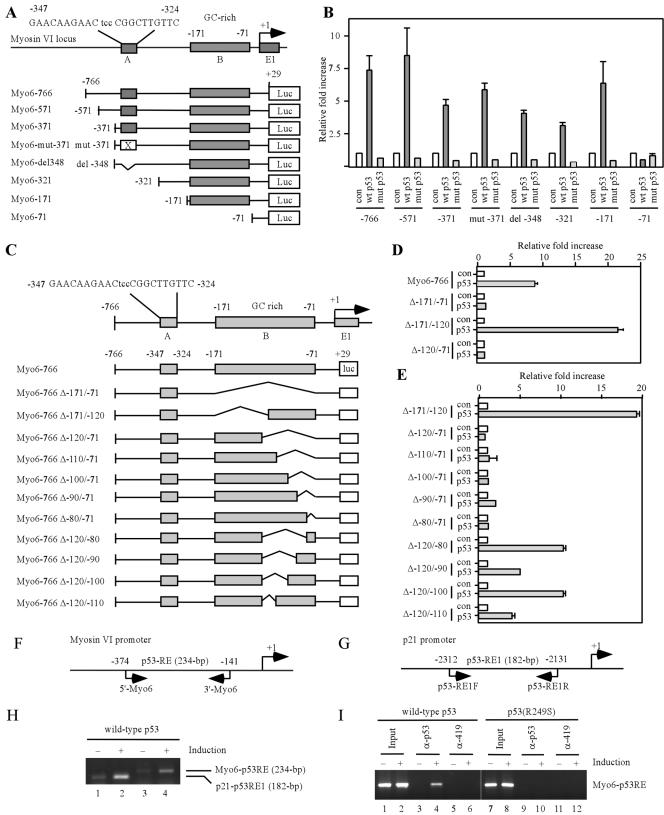
FIG. 3.
Myosin VI is a direct target of the p53 transcription factor. (A) Schematic presentation of the human myosin VI gene locus and luciferase (Luc) reporter constructs. Box A represents a potential p53-binding site from nt −347 to −325, whereas box B is a GC-rich region from nt −171 to −72. (B) The GC-rich region in the myosin VI promoter is responsive to wild-type (wt) p53, but not mutant (mut) p53. The luciferase assay was performed as described in Materials and Methods. con, control. (C) Schematic presentation of 11 additional myosin VI promoter/reporter constructs with deletion in the GC-rich region. (D and E) The GC-rich region is required for p53 transactivation of the myosin VI promoter. (F and G) Schematic representation of the myosin VI and p21 promoters with the locations of the transcription start site, p53-responsive elements, and primers used for ChIP assays. (H) p53 binds directly to the myosin VI promoter. The ChIP assay was performed as described in Materials and Methods. (I) Wild-type p53, but not mutant p53(R249S), binds directly to the myosin VI promoter. α-p53 and α-419, anti-p53 and anti-419 antibodies, respectively.