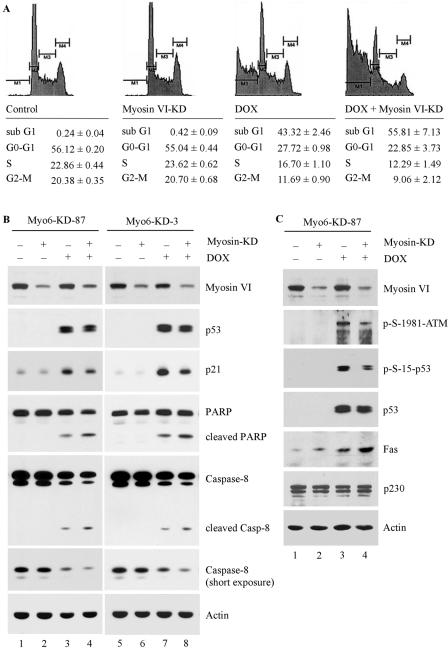
FIG. 8.
Myosin VI knockdown accelerates DNA damage-induced apoptosis. (A) Myo6-KD-87 cells were uninduced (control), induced to express siRNA against myosin VI (myosin VI-KD), treated with 1.0 μg/ml of DOX (DOX), or induced to express siRNA against myosin VI and treated with 1.0 μg/ml of doxorubicin (DOX + Myosin VI-KD). DNA histogram analysis was performed as described in Materials and Methods. The percentage of sub-G1 (M1) cells represents apoptotic cells, whereas M2, M3, and M4 represent cells in G0-G1, S, and G2-M, respectively. (B) DNA damage-induced apoptotic response is enhanced by myosin VI knockdown. Both Myo6-KD-87 and Myo6-KD-3 cells, which were uninduced or induced to express siRNA against myosin VI, were untreated or treated with 1.0 μg per ml of doxorubicin. The expression level of myosin VI, p53, p21, PARP, caspase 8, and actin was quantified by Western blot analysis. (C) Knockdown of myosin VI leads to impaired phosphorylation of p53 via ATM and increased expression of Fas, a target of p53. The experiment was performed as in panel B.