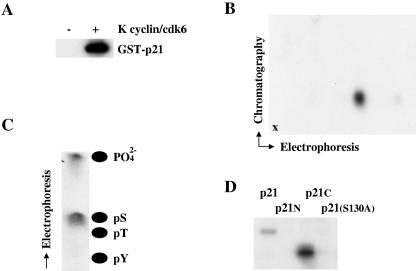
FIG. 1.
K cyclin promotes the phosphorylation of p21Cip1 on serine 130 in vitro. (A) K cyclin/cdk6 was expressed in Sf9 cells by infection with recombinant baculoviruses and used in kinase assays with [γ-32P]ATP and GST-p21Cip1 from bacteria as a substrate. Sf9 cells infected with wild-type baculovirus were used for the negative control. Products of the phosphorylation reactions were resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to autoradiography. (B) GST-p21Cip1 phosphorylated by K cyclin/cdk6 was subject to two-dimensional tryptic phosphopeptide mapping with electrophoresis in the horizontal direction and chromatography in the vertical direction. The point of sample application is marked by “x.” (C) The phosphopeptide shown in panel B was eluted from the cellulose plate and subjected to acid hydrolysis. The resulting hydrolysate was resolved by electrophoresis and subjected to autoradiography. The positions of phosphoamino acid standards are shown. (D) Wild-type and indicated mutant forms of p21Cip1 [N indicates p21(1-103) and C indicates p21(102-164)] were synthesized in bacteria as GST fusion proteins and used as substrates in kinase reactions with K cyclin/cdk6, as shown in panel A.