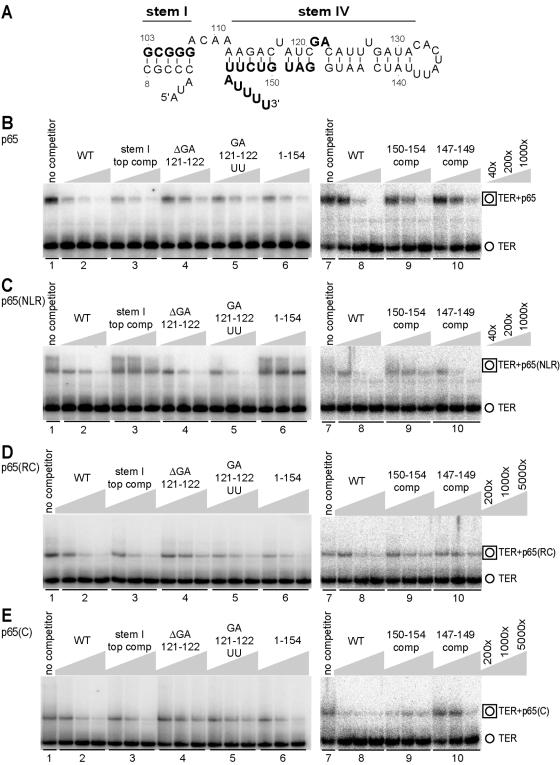
FIG. 3.
Distinct TER binding specificities of p65 domains. (A) TER variants in the stem I/IV region. TER sequence in the stem I/IV region is shown with residues in bold type indicating the positions of sequence substitution or deletion described in the text. (B through E) EMSA competition with WT and variant TERs. Unlabeled TERs were added at the excess concentrations over radiolabeled wild-type TER indicated by the keys on the right. For the binding assays shown in lane sets 1 through 6 or lane sets 7 through 10, the p65, p65(NLR), p65(RC), and p65(C) competitions were performed in parallel with additional controls not shown. We note that, for lane set 9 of panel E, the first lane has less of the mobility shift complex than was detected in a duplicate set of reaction mixtures electrophoresed on the same gel. EMSAs in panels 1 through 6 used 0.2 nM p65, 40 nM p65(NLR), 5 nM p65(RC), and 50 nM p65(C). EMSAs in panels 7 through 10 used 0.4 nM p65, 50 nM p65(NLR), 5 nM p65(RC), and 50 nM p65(C). ΔGA 121-122, deletion of GA 121 and 122.