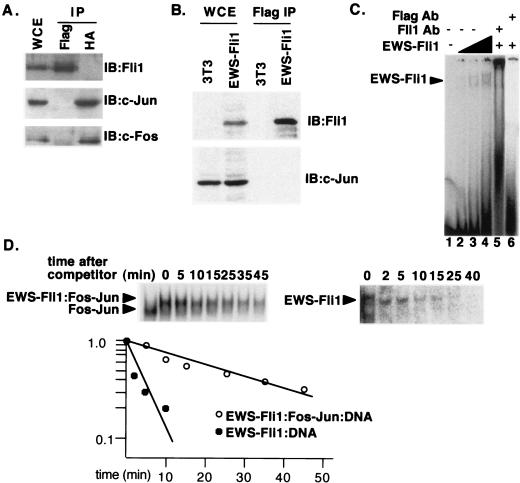
FIG. 2.
EWS and Fli1 interact on DNA but not in solution. (A) HA-c-Fos, c-Jun, and Flag-EWS-Fli1 were coexpressed by transient transfection of 293 cells. Immunoprecipitations (IP) were performed with antibody against either the HA or the Flag tag. The immunoprecipitates were then analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with antibodies directed against c-Fos, c-Jun, or Fli1; the Fli1 antibody recognizes a C-terminal epitope present in EWS-Fli1. WCE, whole-cell extract. (B) Extracts from 3T3 cells or 3T3 cells transformed by stable expression of Flag-EWS-Fli1 were immunoprecipitated with Flag antibody. The resulting extracts were then analyzed for the presence of either c-Jun or EWS-Fli1 by immunoblotting. (C) Recombinant EWS-Fli1 was used in gel shift reactions with the human collagenase probe. The concentrations of EWS-Fli1 were 35, 70, and 140 nM. The two complexes originate from a second low-affinity Ets site in the human collagenase probe. Fli1 and Flag antibodies (Ab) were added to reaction mixtures with 140 nM EWS-Fli1 in lanes 5 and 6, respectively. (D) Gel shift reactions were set up as in Fig. 1 with the human collagenase probe. At time zero, a 200-fold excess of unlabeled competitor was added, and aliquots of the reaction mixture were analyzed by gel shift assay at the indicated times. In the first lane of the left half, no EWS-Fli1 was added. The amount of residual complex was determined by PhosphorImager analysis, and a plot of P-D/P-D0 versus time is shown, where P-D is the amount of the indicated protein-DNA complex at the indicated time, and P-D0 is the amount of the same complex at time zero.