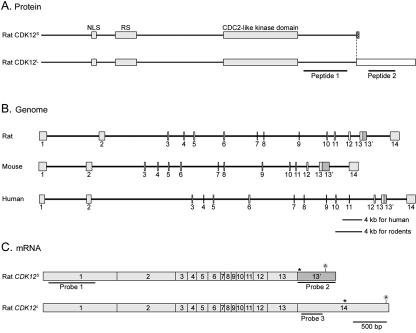
FIG. 1.
Protein, mRNA, and genomic structures of CDK12S and CDK12L. (A) Protein domains of CDK12S and CDK12L. The amino acid sequences of rat CDK12S and CDK12L were analyzed by the MotifScan program. CDK12S and CDK12L share 1,249 amino acids of sequence. They contain a bipartite nuclear localization signal (NLS), an arginine- and serine-rich motif (RS), and a CDC2-like kinase domain (gray boxes). CDK12S and CDK12L display 9 (hatched box) and 235 (blank box) distinct amino acid residues, respectively, at their carboxyl termini. Peptides 1 and 2 were used to generate antisera. (B) Genomic organization of CDK12. The exons were identified by comparing the cDNA sequences with the genomic sequences. The genomic structure of CDK12 contains 14 exons and is conserved between human, mouse, and rat. (C) mRNAs of CDK12S and CDK12L. The CDK12S and CDK12L transcripts share exons 1 to 13, and the CDK12S transcript reads through exon 13′, while the CDK12L transcript splices exon 13 directly to exon 14. The probes used in Northern analysis are underlined. Stop codons are labeled with asterisks. The position of the polyadenylation signal is also indicated.