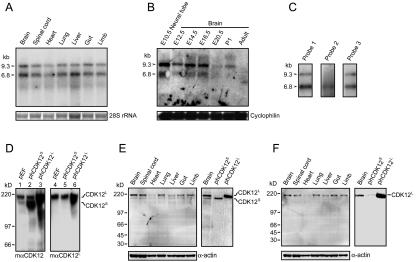
FIG. 2.
Expression of CDK12 in embryonic rat tissues. (A) We used 5 μg of total RNA from various E14.5 rat tissues analyzed by Northern blotting using probe 1 depicted in Fig. 1C. Two major transcripts, 6.8 kb and 9.3 kb (arrowheads), were detected. Ethidium bromide staining of 28S rRNA was used as the loading control. (B) We used 30 μg of total RNA derived from E10.5 neural tube and brain at various developmental stages analyzed by Northern blotting. The membrane was stripped and reprobed with cyclophilin for the loading control. (C) Polyadenylated mRNA from E14.5 rat brain analyzed by Northern blotting using probe 1, probe 2, or probe 3. Probe 1 and probe 3 detected two transcripts, while probe 2 detected only the 6.8-kb transcript. (D) We used 20 μg of cell extracts of HEK293T transfected with control vector (pEF), phCDK12S and phCDK12L to examine the specificity of the mαCDK12 and the mαCDK12L antisera. The mαCDK12 antiserum recognizes both CDK12S and CDK12L, and the mαCDK12L antiserum recognizes only CDK12L. (E) Western analysis of 15 μg of E14.5 rat tissue extracts performed using mαCDK12 (left panel). The sizes of CDK12S and CDK12L detected in the E14.5 brain by the mαCDK12 antiserum are the same as those detected in 4 μg of CDK12S- or CDK12L-overexpressed HEK293T cell lysates (right panel). (F) Western analysis of 15 μg of E14.5 rat tissue extracts performed using mαCDK12L (left panel). The size of CDK12L detected in the E14.5 brain by the mαCDK12L antiserum is the same as that detected in 4 μg of CDK12L-overexpressed HEK293T cell lysates (right panel). Membranes were reprobed with the anti-α-actin antibody as the loading control.