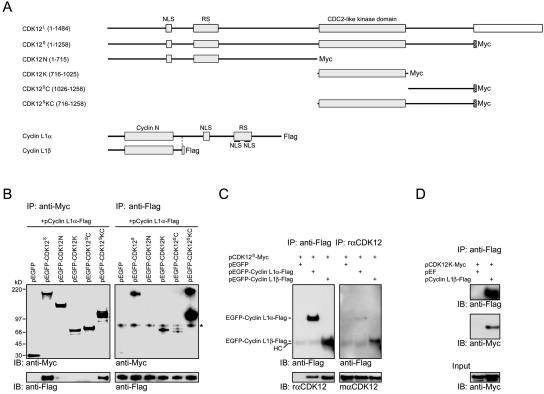
FIG. 4.
Mapping of interaction domains between CDK12 and cyclin L1. (A) Schematic structures of CDK12L, Myc-tagged CDK12S, various Myc-tagged CDK12 truncated constructs, Flag-tagged cyclin L1α, and Flag-tagged cyclin L1β. (B) Lysates of HEK293T cells transfected with various CDK12 truncated constructs and pcyclin L1α-Flag were immunoprecipitated with the anti-Myc antibody. The immunoprecipitates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with the anti-Flag antibody or the rabbit anti-Myc antiserum (left panels). The same lysates were also immunoprecipitated with the anti-Flag antibody. The immunoprecipitates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with the anti-Flag antibody or the rabbit anti-Myc antiserum (right panels). A nonspecific band was recognized by the rabbit anti-Myc antiserum (asterisk). (C) Lysates of HEK293T cells transfected with the plasmids listed above the panel and immunoprecipitated with the anti-Flag antibody. The resulting proteins were then immunoblotted using the rabbit anti-Flag antiserum or the rαCDK12 antiserum (left panels). The same lysates were immunoprecipitated with the rαCDK12 antiserum. The resulting proteins were then immunoblotted using the mαCDK12 antiserum or the anti-Flag antibody (right panels). A faint band corresponding to the heavy chain (HC) of antibodies used in the immunoprecipitation was detected by the secondary antibodies. (D) Lysates of HEK293T cell transfected with pCDK12K-Myc and pEF or pcyclin L1β-Flag were immunoprecipitated with the anti-Flag antibody. The resulting proteins were then immunoblotted using the anti-Flag antibody or the rabbit anti-Myc antiserum.