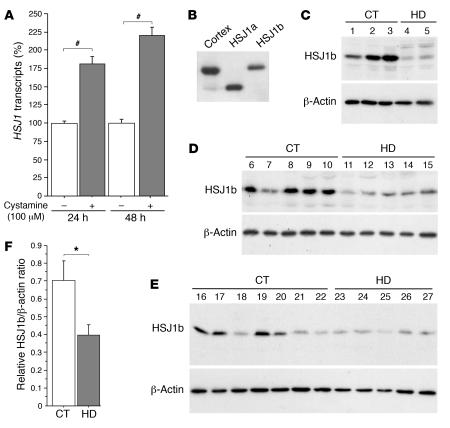
Figure 1. Cystamine increases HSJ1 transcript levels in neuronal cells, while HSJ1b is decreased in postmortem brain extracts from HD patients.
(A) Data revealed a statistically significant increase in HSJ1 transcripts induced by cystamine treatment in comparison to control at 24 hours (Student’s t test, t[21] = 5.77; P < 0.0001) and at 48 hours (Student’s t test, t[10] = 9.88; P < 0.0001). (B) Protein extracts prepared from 1 control human cortical postmortem sample and from HEK 293T cells transfected with HSJ1a or HSJ1b were immunoblotted with an anti-HSJ1 antibody. The major brain isoform of HSJ1 proteins was the HSJ1b isoform. (C–E) Protein extracts were prepared from whole striatum (C), putamen (D), and caudate nucleus (E) of control (CT) and HD individuals and analyzed as in B. Immunoblotting with an anti–β-actin antibody was used as a control. (F) Quantification of the Western blots presented in C–E showed a statistically significant decrease in the protein level of HSJ1b in HD samples (n = 12) compared with control samples (n = 15) (Student’s t test, t[25] = 2.33; P = 0.028). *P < 0.05, #P < 0.0001.