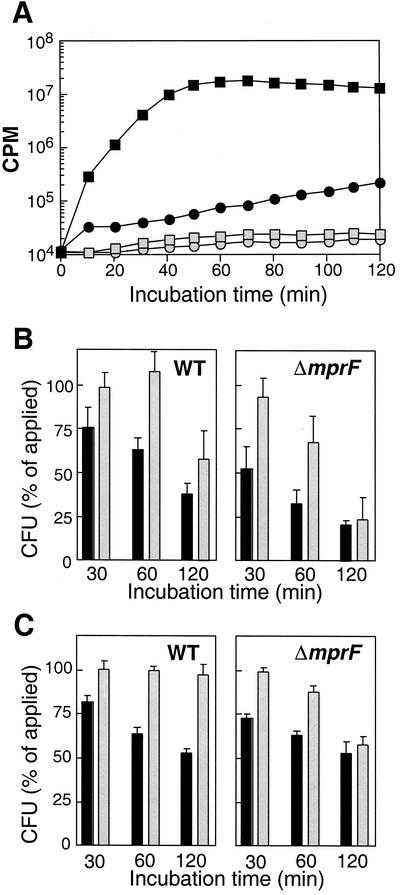
FIG. 2.
Inhibition of the respiratory burst (A) and its impact on killing of S. aureus by human neutrophils (B) or monocytes (C). (A) The respiratory burst of neutrophils was monitored by measuring luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence in the presence (open symbols) or absence (black symbols) of the NADPH oxidase inhibitor DPI. Neutrophils were not challenged (circles) or were challenged with opsonized S. aureus (squares) The results of a representative experiment are shown. (B and C) The numbers of viable opsonized wild-type (WT) and ΔmprF mutant CFU after 30, 60, or 120 min of incubation with human neutrophils (B) or monocytes (C) in the absence (black bars) or presence (gray bars) of DPI are expressed as percentages of the initial counts. The values shown are the means and standard errors of at least three independent experiments.