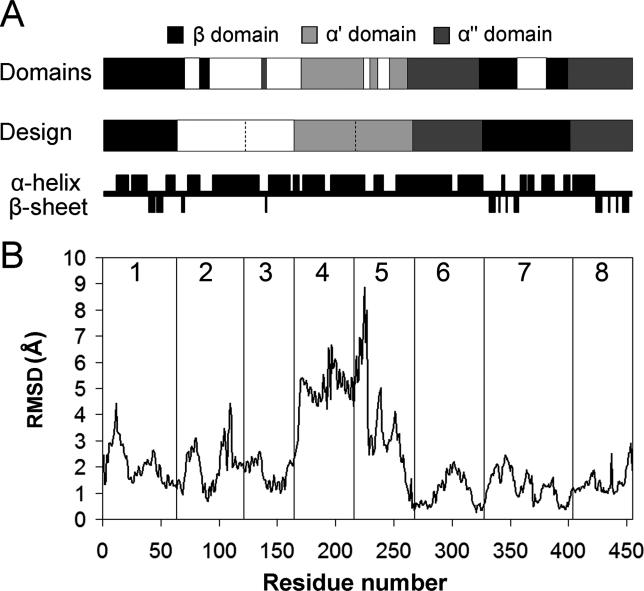
Figure 3. Comparison of Library Design to Domains, Dynamics, and Secondary Structure of CYP102A1.
(A) Crossovers in the library designed using the SCHEMA energy function capture domain boundaries of CYP102A1 determined from molecular dynamics simulations [ 27]. Crossovers between blocks 2–3, 4–5, 5–6, and 7–8 lie within α-helices. (Secondary structure assignment is based on the CYP102A1 crystal structure [ 24]).
(B) Plot of the RMSD between the backbone atoms of the substrate-bound (closed) and unbound (open) structures of CYP102A1. The RMSD was calculated by comparing molecule B of the substrate-free structure [ 29] and molecule A of the structure bound to palmitoleic acid [ 26] using Swiss PDB Viewer. Vertical lines designate crossover locations and blocks are numbered. Crossovers between blocks 1–2, 5–6, 6–7, and 7–8 occur at positions that move < 1.2 Å between the two structures. Crossover 3–4 is located next to a region of high identity and may be shifted towards the N-terminus by up to 14 residues and still produce the same chimeras. This shift allows it to occur at a position which moves < 1.2 Å.