Fig. 1.
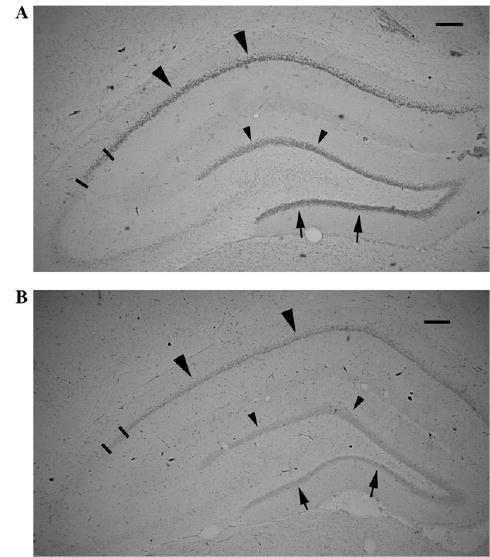
GR expression in the dorsal hippocampus is decreased by prenatal corticosteroid treatment. (A) PN20 control male rat prenatally exposed to saline on E15. GR immunohistochemistry with DAB visualization. Large arrowheads point to the GR expression in the CA1 area; arrows point to the inner blade of the dentate gyrus granule cells. Small arrowheads point to the outer blade of dentate gyrus granule cells. Bars limit the CA2 area. Scale bar = 200 μm. (B) PN20 male rat prenatally exposed to 2 × 0.4 mg/kg betamethasone on E15. Immunohistochemical staining has been run in the same dish as the section shown in (A). Expression of GR in all areas marked by large arrowheads (CA1), arrows (inner granule cell blade), and small arrowheads (outer granule cell blade) as well as in the CA2 (bar limited) is decreased consistently with findings of decreased hippocampal GR after prenatal dexamethasone treatment [43]. Scale bar = 200 μm.
