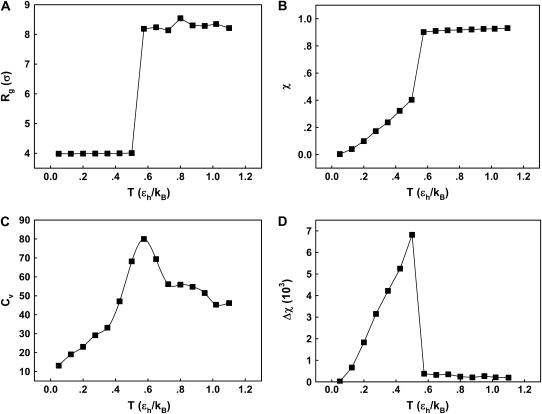
FIGURE 2.
Thermodynamics properties of the Gō-like protein in a dilute solution. Protein folding is characterized by a reduction of the protein radius of gyration (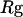 ) and by the structure overlap function (
) and by the structure overlap function (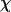 ). The collapse temperature is determined from
). The collapse temperature is determined from 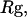 corresponding to a maximum heat capacity; the folding temperature is determined from
corresponding to a maximum heat capacity; the folding temperature is determined from 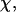 corresponding to a maximum in the structural fluctuation
corresponding to a maximum in the structural fluctuation 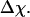 (A)
(A) 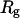 versus T. (B)
versus T. (B) 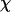 versus T. (C)
versus T. (C) 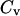 versus T. (D)
versus T. (D) 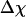 versus T.
versus T.