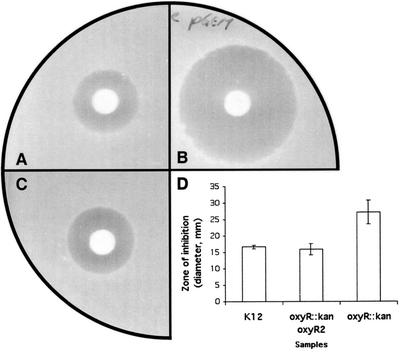
FIG. 6.
H2O2 disk assay. Photos showing the zones of inhibition by H2O2 in E. coli K-12 (wild type) (A), GS09 (oxyR::kan mutant) (B), and E. coli K-12 strain GS09 complemented with the oxyR gene (pHJToxyR-1) from N. gonorrhoeae (C). (D) Histogram showing the results of H2O2 disk assay in E. coli. In the assay, cells were grown on LB agar in the presence or absence of 0.5 mM isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG). Sensitivity to H2O2 was measured by the zone of inhibition (diameter). The zone of inhibition was measured in three dimensions, and the mean values and standard deviations were calculated. The y-axis error bars each indicate ±1 standard deviation of the mean. Student's t test was performed to determine the statistical significance among different samples. The E. coli K-12 oxyR::kan mutant was significantly more sensitive to H2O2 than the wild type and the complemented strain (P = 0.03315 and 0.01757, respectively).