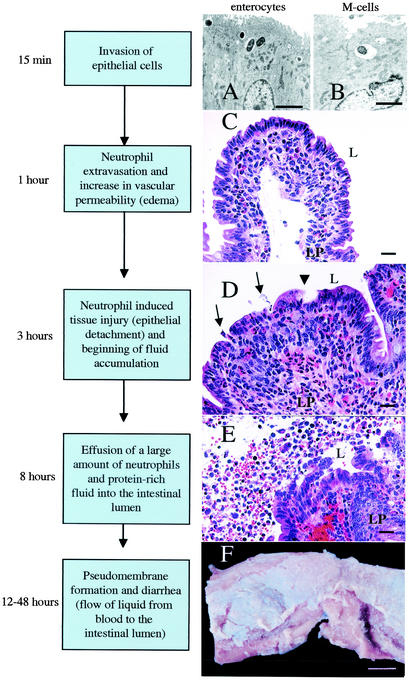
FIG. 2.
Current model of the series of events leading to an inflammatory diarrhea during Salmonella serotype Typhimurium infection of calves. (A) Transmission electron micrograph of bovine Peyer's patch at 15 min after infection of a ligated ileal loop with Salmonella serotype Typhimurium strain ATCC 14028 (109 CFU/loop). Ruffling of the brush border of an enterocyte and bacterial internalization into membrane-bound vacuoles can be seen (bar = 2.5 μm). (B) Transmission electron micrograph of bovine Peyer's patch at 15 min after infection of a ligated ileal loop with Salmonella serotype Typhimurium strain ATCC 14028 (109 CFU/loop). An M cell in the follicle-associated epithelium containing an internalized bacterium is shown (bar = 2.5 μm). (C) Focal infiltration of neutrophils in the lamina propria (LP) of an absorptive villus in bovine Peyer's patches at 1 h after infection of a ligated ileal loop with Salmonella serotype Typhimurium strain ATCC 14028 (109 CFU/loop) (bar = 20 μm). (D) Blunting of absorptive villus 3 h after infection of a ligated ileal loop with Salmonella serotype Typhimurium strain ATCC 14028 (109 CFU/loop). Note the hemorrhage and infiltration of the lamina propria with neutrophils. Arrows indicate areas where neutrophils transmigrate into the intestinal lumen (L). The arrowhead indicates the detachment of surface epithelial cells at the tip of an absorptive villus (bar = 20 μm). (E) Presence of a large number of neutrophils in the intestinal lumen (L) at 8 h postinfection of a ligated ileal loop with Salmonella serotype Typhimurium strain ATCC 14028 (109 CFU/loop). Note the hemorrhage, injury to the intestinal epithelium, and detached enterocytes (bar = 20 μm). (F) Gross pathology of the terminal ileum of a calf at 48 h after oral infection with Salmonella serotype Typhimurium strain ATCC 14028 (1010 CFU). Note the pseudomembrane formation over a bovine Peyer's patch (bar = 1 cm).