Full text
PDF


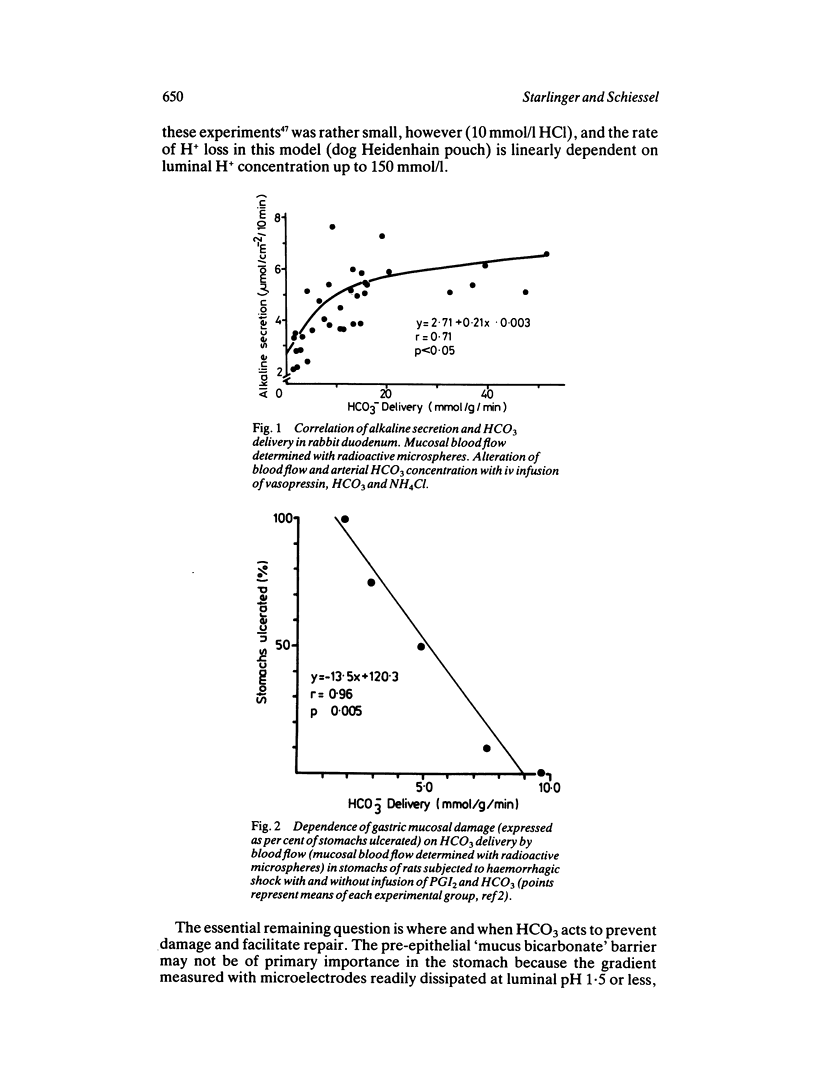




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A., Hutton D., McQueen S., Garner A. Dimensions of gastroduodenal surface pH gradients exceed those of adherent mucus gel layers. Gastroenterology. 1983 Aug;85(2):463–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barzilai A., Schiessel R., Kivilaakso E., Matthews J. B., Fleischer L. A., Bartzokis G., Silen W. Effect of 16-16-dimethyl-prostaglandin E2 on ulceration of isolated amphibian gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jun;78(6):1508–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruggeman T. M., Wood J. G., Davenport H. W. Local control of blood flow in the dog's stomach: vasodilatation caused by acid back-diffusion following topical application of salicylic acid. Gastroenterology. 1979 Oct;77(4 Pt 1):736–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushell M., O'Brien P. Acid-base imbalance and ulceration in the cold restrained rat. Surgery. 1982 Mar;91(3):318–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter K. J., Farley P. C., Ritchie W. P., Jr Effect of topical bile acids on gastric surface epithelial cells. Surgery. 1984 Aug;96(2):196–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung L. Y., Moody F. G., Reese R. S. Effect of aspirin, bile salt, and ethanol on canine gastric mucosal blood flow. Surgery. 1975 Jun;77(6):786–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung L. Y., Porterfield G. Protection of gastric mucosa against acute ulceration by intravenous infusion of sodium bicarbonate. Am J Surg. 1979 Jan;137(1):106–110. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(79)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collan Y., Kivilaakso E., Kalima T. V., Lempinen M. Ultrastructural changes in the gastric mucosa following hemorrhagic shock in pigs. Circ Shock. 1977;4(1):13–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton M. T., Kauffman G. L., Jr, Schlegel J. F., Code C. F., Steinbach J. H. Gastric bicarbonate appearance with ethanol ingestion. Mechanism and significance. Dig Dis Sci. 1983 May;28(5):449–455. doi: 10.1007/BF02430534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemstrom G., Garner A. Gastroduodenal HCO3(-) transport: characteristics and proposed role in acidity regulation and mucosal protection. Am J Physiol. 1982 Mar;242(3):G183–G193. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.242.3.G183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fändriks L. Sympatho-adrenergic inhibition of vagally induced gastric motility and gastroduodenal HCO-3 secretion in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Dec;128(4):555–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb08012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon B., Browning J., O'Brien P., Rogers P. Mucosal microvascular architecture of the fundus and body of human stomach. Gastroenterology. 1984 May;86(5 Pt 1):866–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groll A., Simon J. B., Wigle R. D., Taguchi K., Todd R. J., Depew W. T. Cimetidine prophylaxis for gastrointestinal bleeding in an intensive care unit. Gut. 1986 Feb;27(2):135–140. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.2.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heylings J. R., Garner A., Flemström G. Regulation of gastroduodenal HCO-3 transport by luminal acid in the frog in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1984 Mar;246(3 Pt 1):G235–G242. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.3.G235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg J. I., Hogan D. L., Koss M. A., Selling J. A. Human duodenal mucosal bicarbonate secretion. Evidence for basal secretion and stimulation by hydrochloric acid and a synthetic prostaglandin E1 analogue. Gastroenterology. 1986 Aug;91(2):370–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg J. I., Smedfors B., Johansson C. Effect of graded doses of intraluminal H+, prostaglandin E2, and inhibition of endogenous prostaglandin synthesis on proximal duodenal bicarbonate secretion in unanesthetized rat. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jan;88(1 Pt 2):303–307. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80184-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh M., Paulsen G., Guth P. H. Hemorrhagic shock and acid gastric injury in the rat. Comparison of gross and histologic findings. Gastroenterology. 1986 May;90(5 Pt 1):1103–1110. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90374-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivilaakso E., Barzilai A., Schiessel R., Fromm D., Silen W. Experimental ulceration of rabbit antral mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jan;80(1):77–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivilaakso E. Contribution of ambient HCO3- to mucosal protection and intracellular pH in isolated amphibian gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1284–1289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivilaakso E., Fromm D., Silen W. Effect of the acid secretory state on intramural pH of rabbit gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1978 Oct;75(4):641–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivilaakso E., Fromm D., Silen W. Relationship between ulceration and intramural pH of gastric mucosa during hemorrhagic shock. Surgery. 1978 Jul;84(1):70–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivilaakso E. High plasma HCO3-protects gastric mucosa against acute ulceration in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1981 Nov;81(5):921–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Bilski J., Tasler J., Laskiewicz J. Gastroduodenal alkaline response to acid and taurocholate in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 1):G149–G154. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.247.2.G149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Thor P. Relation between duodenal alkaline secretion and motility in fasted and sham-fed dogs. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 1):G591–G596. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.5.G591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung F. W., Itoh M., Hirabayashi K., Guth P. H. Role of blood flow in gastric and duodenal mucosal injury in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jan;88(1 Pt 2):281–289. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. A., Gaskill H. V., 3rd, Sirinek K. R. Gastric mucosal cytoprotection by splanchnicectomy is based on protection of gastric mucosal blood flow. J Trauma. 1983 Apr;23(4):278–284. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198304000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGreevy J. M., Moody F. G. Focal microcirculatory changes during the production of aspirin-induced gastric mucosal erosions. Surgery. 1981 Mar;89(3):337–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGreevy J. M., Moody F. G. Protection of gastric mucosa against aspirin-induced erosions by enhanced blood flow. Surg Forum. 1977;28:357–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen S., Hutton D., Allen A., Garner A. Gastric and duodenal surface mucus gel thickness in rat: effects of prostaglandins and damaging agents. Am J Physiol. 1983 Sep;245(3):G388–G393. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.3.G388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mersereau W. A., Hinchey E. J. Interactions of gastric blood flow, barrier breaker, and hydrogen ion back diffusion during ulcer formation in the rat. Surgery. 1978 Mar;83(3):248–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. P., Harding R. K., Wallace J. L. A functional model for extracellular gastric mucus in the rat. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1984;46(3):239–251. doi: 10.1007/BF02890313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. A., Haedicke G. J., Bulkley G. B., Kvietys P. R., Granger D. N. Relationship between acid secretion and blood flow in the canine stomach: role of oxygen consumption. Gastroenterology. 1983 Sep;85(3):529–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie W. P., Jr Acute gastric mucosal damage induced by bile salts, acid, and ischemia. Gastroenterology. 1975 Apr;68(4 Pt 1):699–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie W. P., Jr, Shearburn E. W., 3rd Influence of isoproterenol and cholestyramine on acute gastric mucosal ulcerogenesis. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jul;73(1):62–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross I. N., Bahari H. M., Turnberg L. A. The pH gradient across mucus adherent to rat fundic mucosa in vivo and the effect of potential damaging agents. Gastroenterology. 1981 Oct;81(4):713–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross I. N., Turnberg L. A. Studies of the 'mucus-bicarbonate' barrier on rat fundic mucosa: the effects of luminal pH and a stable prostaglandin analogue. Gut. 1983 Nov;24(11):1030–1033. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.11.1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. J., Ayalon A., Roll M., Soll A. H. The apical surface of canine chief cell monolayers resists H+ back-diffusion. Nature. 1985 Jan 3;313(5997):52–54. doi: 10.1038/313052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiessel R., Merhav A., Matthews J. B., Fleischer L. A., Barzilai A., Silen W. Role of nutrient HCO3(-) in protection of amphibian gastric mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1980 Dec;239(6):G536–G542. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.239.6.G536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starlinger M., Jakesz R., Matthews J. B., Yoon C., Schiessel R. The relative importance of HCO3- and blood flow in the protection of rat gastric mucosa during shock. Gastroenterology. 1981 Oct;81(4):732–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starlinger M., Matthews J., Yoon C., Wenzl E., Feil W., Schiessel R. The effect of acid perfusion on mucosal blood flow and intramural pH of rabbit duodenum. Surgery. 1987 Apr;101(4):433–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starlinger M., Paradiso A. M., Machen T. E. Steady state regulation of intracellular pH in isolated rabbit gastric glands. Roles for Na/H and Cl/OH (HCO3) exchange. Gastroenterology. 1987 Apr;92(4):957–965. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90970-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starlinger M., Schiessel R., Hung C. R., Silen W. H+ back diffusion stimulating gastric mucosal blood flow in the rabbit fundus. Surgery. 1981 Feb;89(2):232–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanes K., Ito S., Takeuchi K., Silen W. Restitution of the surface epithelium of the in vitro frog gastric mucosa after damage with hyperosmolar sodium chloride. Morphologic and physiologic characteristics. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jun;82(6):1409–1426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanes K., Takeuchi K., Ito S., Silen W. Effect of luminal pH and nutrient bicarbonate concentration on restitution after gastric surface cell injury. Surgery. 1983 Sep;94(3):494–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi K., Magee D., Critchlow J., Matthews J., Silen W. Studies of the pH gradient and thickness of frog gastric mucus gel. Gastroenterology. 1983 Feb;84(2):331–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi K., Merhav A., Silen W. Mechanism of luminal alkalinization by bullfrog fundic mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):G377–G388. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.243.5.G377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi K., Okabe S. Role of luminal alkalinization in repair process of ethanol-induced mucosal damage in rat stomach. Dig Dis Sci. 1983 Nov;28(11):993–1000. doi: 10.1007/BF01311728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace J. L., Whittle B. J. Role of mucus in the repair of gastric epithelial damage in the rat. Inhibition of epithelial recovery by mucolytic agents. Gastroenterology. 1986 Sep;91(3):603–611. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90629-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzl E., Feil W., Starlinger M., Schiessel R. Alkaline secretion. A protective mechanism against acid injury in rabbit duodenum. Gastroenterology. 1987 Mar;92(3):709–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J., Kauffman G. L., Moncada S. Vasoconstriction with thromboxane A2 induces ulceration of the gastric mucosa. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):472–474. doi: 10.1038/292472a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J. Mechanisms underlying gastric mucosal damage induced by indomethacin and bile-salts, and the actions of prostaglandins. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Jul;60(3):455–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07522.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


