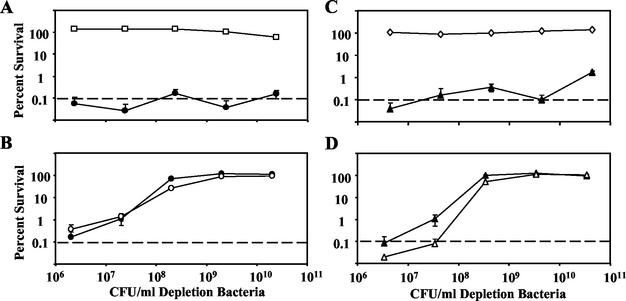
FIG. 7.
Activation and depletion of complement by the B. bronchiseptica wild type (A, RB50, open squares) or Δwbm mutant (B, RB50Δwbm, open circles) with the B. bronchiseptica Δwbm mutant (RB50 Δwbm Gmr, closed circles) as a sensitive target with which to detect remaining complement activity. Activation of complement by the B. parapertussis wild type (C, CN2591, open diamonds) or Δwbm mutant (D, CN259Δwbm, open triangles) with the B. parapertussis Δwbm mutant (CN2591 Δwbm Gmr; closed triangles) as a sensitive target with which to detect remaining complement activity. All bacteria were grown to mid-log phase in Stainer-Scholte broth and diluted in 1× PBS. Depletion bacteria (streptomycin resistant) were incubated in 10% naive-rabbit serum at various concentrations between 106 and 1011 CFU/ml for 10 min at 37°C. Target bacteria (5 μl of 100 CFU of streptomycin- and gentamicin-resistant bacteria per ml) were then added to the depletion reaction mixture, which was incubated at 37°C for an additional hour. Percent survival of both the depletion and target bacteria is compared to that of a PBS control with the standard error and plotted against the number of CFU of depletion bacteria per milliliter of reaction mixture (n = 4). The lower limit of detection by the assay is indicated by a dashed line.