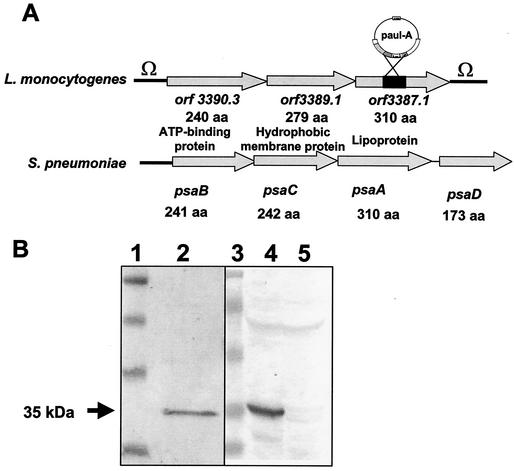
FIG. 1.
(A) Comparison of the genetic organization of the lpeA operon of L. monocytogenes with that of the psaA operon of S. pneumoniae. The lpeA operon is framed by two terminators (Ω). The lpeA gene is the third of the operon (orf3387.1), and there is no homologue for the regulator psaD in the genome of L. monocytogenes. lpeA encodes a lipoprotein homologous to PsaA of S. pneumoniae. Shown is the insertion of the promoterless aphA-3 cassette on plasmid pAUL-A into the lpeA gene. (B) Western blot analysis of the mutant of L. monocytogenes lacking lpeA. Bacterial extracts from EGD-e or lpeA mutant were tested with a monoclonal antibody (MAb) anti-ScaA, a PsaA homologue of S. gordonii. (Left panel) The MAb recognizes a 35-kDa band from a bacterial extract of S. gordonii. (Right panel) The MAb recognizes a 35-kDa band in wild-type EGD-e and does not react against the extracts from the lpeA mutant of L. monocytogenes. Lanes: 1 and 3, molecular markers; 2, S. gordonii; 4, EGD-e; 5, lpeA mutant.