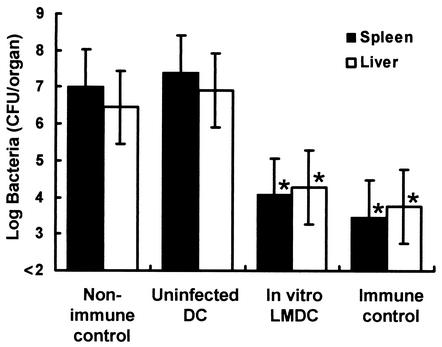
FIG. 1.
Acquired resistance to a lethal L. monocytogenes infection in mice immunized with in vitro L. monocytogenes-pulsed DCs. Spleens were removed from uninfected mice, and CD11c+ DCs were purified. The DCs were incubated with 10 CFU of viable L. monocytogenes per DC as described in the text. After killing of viable L. monocytogenes by antibiotics, naive mice were immunized with 105 in vitro-infected DCs (In vitro LMDC) or uninfected DCs. Nonimmune control mice were injected with PBS only. These mice were challenged intravenously with 5 × 106 CFU of L. monocytogenes 4 weeks later. The numbers of bacteria in the spleens and livers of the mice were determined at 48 h after the challenge. The immune control mice were directly immunized with 105 CFU of L. monocytogenes. Each result represents the mean ± the standard deviation of a group of six mice from two independent experiments. An asterisk indicates a significant difference from the value for the nonimmune control group (P < 0.01).