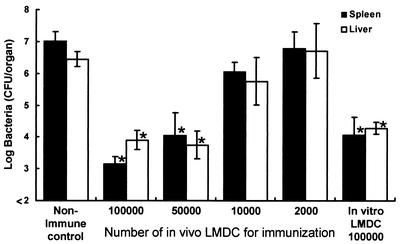
FIG. 6.
Dependence of acquired resistance to a lethal L. monocytogenes infection on the number of L. monocytogenes-infected DCs (LMDC) used for immunization. Mice were infected intravenously with 5 × 105 CFU of L. monocytogenes, and their spleens were removed 48 h later. Naive mice were immunized with 105, 5 × 104, 104, or 2 × 103 purified DCs from L. monocytogenes-infected mice or with 105 in vitro-pulsed DCs. Nonimmune control mice were injected with PBS only. Mice of each group were challenged with 5 × 106 CFU of L. monocytogenes intravenously 4 weeks later. The numbers of bacteria in the spleens and livers of the mice were determined at 48 h after the challenge. Each result represents the mean ± the standard deviation for a group of six mice from two independent experiments. An asterisk indicates a significant difference from the value for the nonimmune control group (P < 0.01).