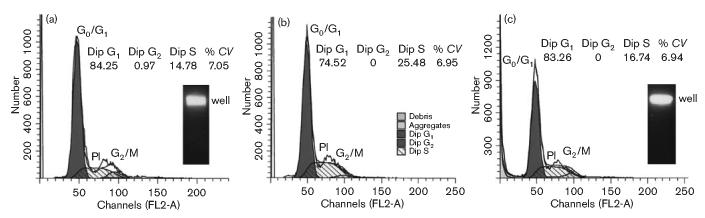
Fig. 2.
Examination of CDT-treated cementoblasts for cell-cycle arrest and dsDNA damage. Cementoblast cultures (1 × 106 cells) were left untreated (a) or were treated (b, c) with medium containing protein extract from E. coli BL21(DE3)(pET15bcdt) at a concentration of 18.4 μg ml−1. Cell nuclei were collected and stained at 48 h (b) and 72 h (c) post-intoxication. Cell-cycle profiles obtained by flow cytometry are shown. The DNA profile determined by propidium iodide staining is shown as the open tracing marked PI. G0/G1 and G2/M (filled) and S (hatched) peaks were determined by computer analysis. The percentages of cells in the population in the diploid G1, diploid G2 and diploid S states are shown. CV is the coefficient of variance. The insets show PFGE of untreated and CDT-treated (72 h) cultures. Gels were stained with ethidium bromide. The position of the wells in the agarose gel is marked.