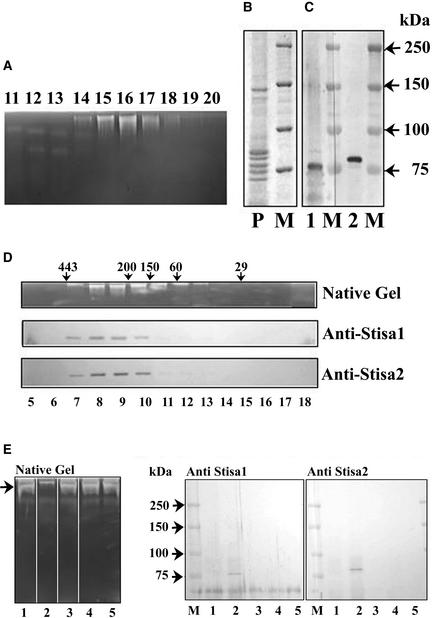
Figure 7.
Presence of Stisa1 and Stisa2 Proteins in Partially Purified Isoamylase.
Isoamylase activity was purified by an initial precipitation step (brought about by either ammonium sulfate or pH 5), followed by ion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-Sepharose and MonoQ and gel filtration on Superose 12.
(A) Fractions (lanes 11 to 20) from the MonoQ separation (after protein precipitation at pH 5) were subjected to electrophoresis on native, amylopectin-containing gels to show the isoamylase activity by staining with iodine solution.
(B) Coomassie blue staining of an SDS–polyacrylamide gel of protein from MonoQ fraction 16 (P). M indicates protein size markers with molecular mass in kD.
(C) Protein from MonoQ fraction 16 separated on SDS–polyacrylamide gels and transferred to nitrocellulose probed with antiserum to Stisa1 (lane 1) or Stisa2 (lane 2). M indicates protein size markers with molecular mass in kD.
(D) Fractions after Superose 12 chromatography, from a preparation using an ammonium sulfate precipitation. Isoamylase activity, as determined by native amylopectin gel separation followed by iodine staining, is compared with the presence of Stisa1 and Stisa2 peptides in the fractions, as determined by electrophoresis of the fractions (lanes 5 to 18) on SDS–polyacrylamide gels, transfer to nitrocellulose, and development with the anti-Stisa1 and anti-Stisa2 antisera. Arrows indicate molecular mass in kD of proteins eluting at particular points, as determined using size standards.
(E) Native, amylopectin-containing gel and immunoblots of SDS–polyacrylamide gels of supernatant fractions after incubation with antisera to Stisa1 and Stisa2. Partially purified isoamylase was incubated with protein A–Sepharose that had been preincubated as follows: lane 1, Stisa1 antiserum; lane 2, Stisa 2 antiserum; lane 3, Stisa1 preimmune serum; lane 4, Stisa2 preimmune serum; lane 5, BSA at 20 mg/mL in tuber extraction medium plus 0.15 M KCl. The left gel shows the isoamylase activity (arrow) remaining in the supernatants for these different treatments determined on amylopectin gels. Lane 2 shows the loss of the isoamylase band caused by the interaction of the Stisa2 antibody with the native isoamylase. The proteins from the antisera/protein A precipitations were recovered by centrifugation of the Sepharose and release by boiling in SDS sample buffer. These proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with antiserum to Stisa1 (middle gel) or Stisa2 (right gel) as indicated. Both Stisa1 and Stisa2 peptides were recovered from the interaction between the Stisa2 antiserum and the isoamylase (lane 2 in both gels). Prestained markers are shown (M), with molecular masses indicated in kD.