Abstract
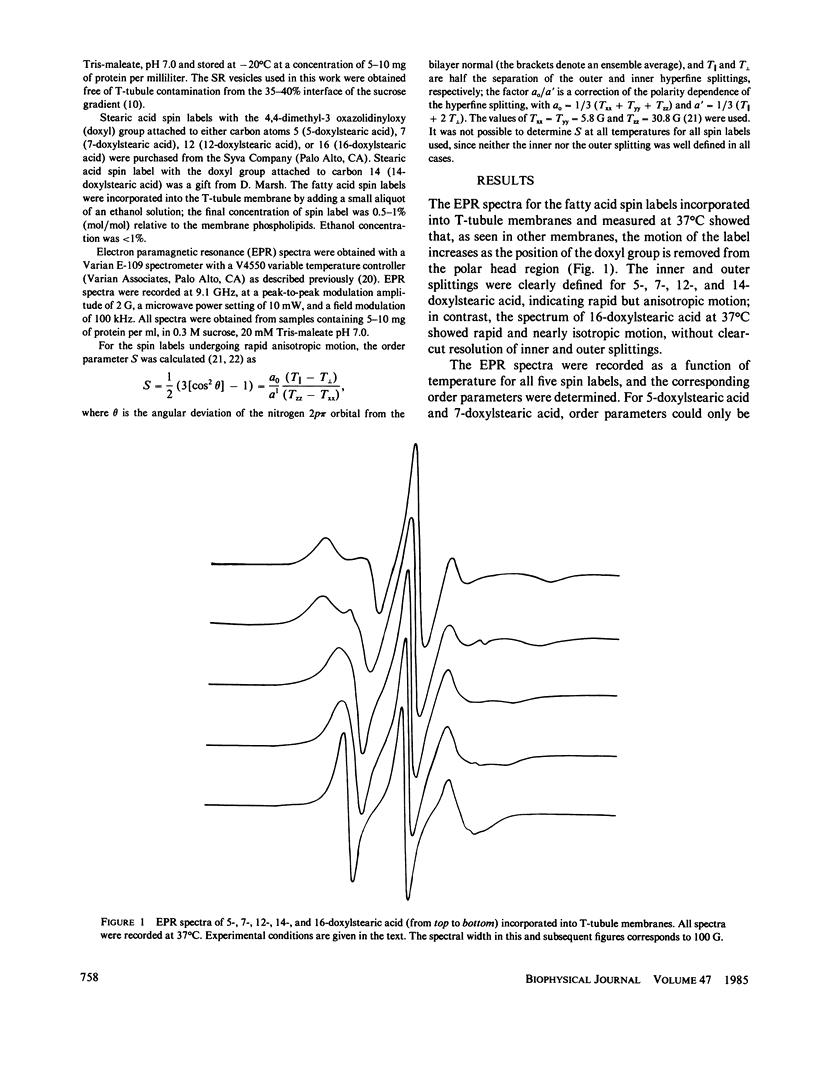
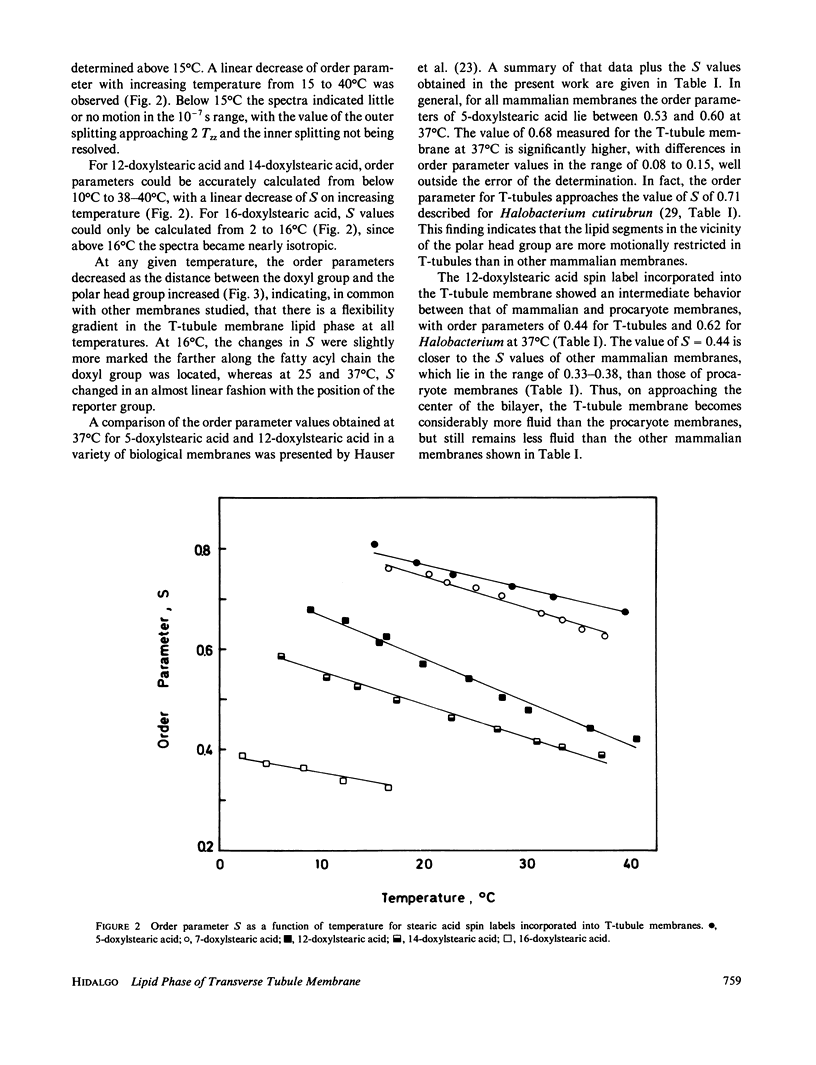
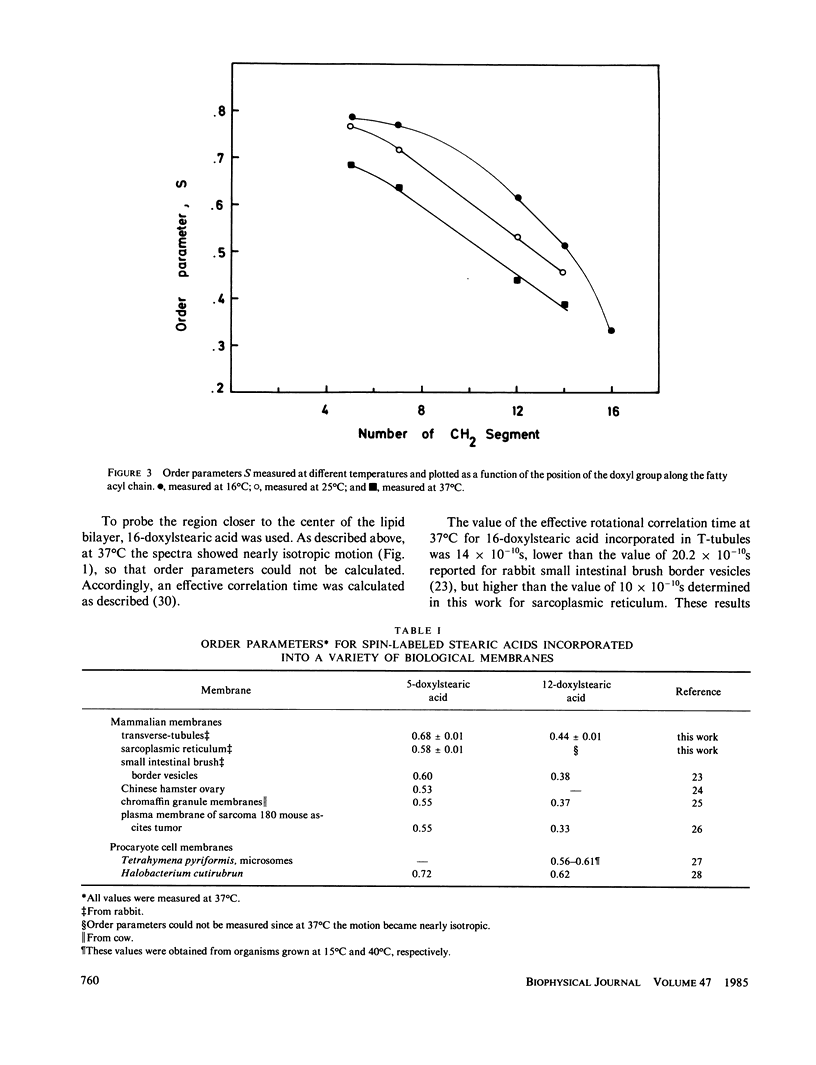
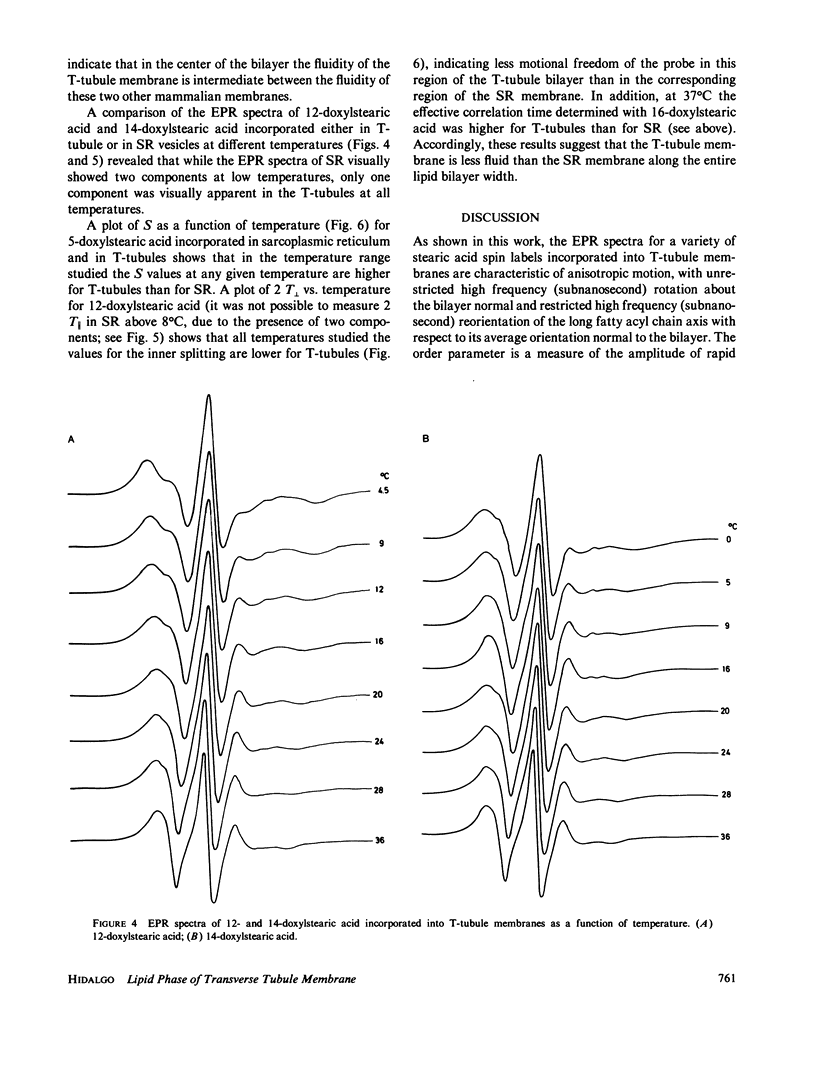
The lipid phase of transverse tubule membrane was probed with a variety of fatty acid spin labels. The motion of the probe increased as the distance between the spin label and polar head group increased, in agreement with results reported in other membranes. The value of the order parameter at 37 degrees C for a fatty acid spin label containing the label attached to its fifth carbon atom was closer to values reported for bacterial membranes than to the lower values reported for other mammalian membranes. Order parameters for spin labels containing the label nearer to the center of the bilayer were closer to the values reported in other mammalian membranes than to values reported for bacterial membranes. These results indicate that the lipid segments in the vicinity of the polar head group, and less so those near the center of the bilayer, are motionally more restricted in transverse tubules than in other mammalian membranes. In particular, the lipid phase of the transverse tubule membrane is less fluid than that of the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. A possible role of the high cholesterol content of transverse tubules in generating the lower fluidity of its lipid phase is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bales B. L., Lesin E. S., Oppenheimer S. B. On cell membrane lipid fluidity and plant lectin agglutinability. A spin label study of mouse ascites tumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 1;465(2):400–407. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L., Weigele J. B., Chalikian D. M., Murphy L. E. Muscle surface membranes: preparative methods affect apparent chemical properties and neurotoxin binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 5;550(1):59–76. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastian J., Nakajima S. Action potential in the transverse tubules and its role in the activation of skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Feb;63(2):257–278. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt N. R., Caswell A. H., Brunschwig J. P. ATP-energized Ca2+ pump in isolated transverse tubules of skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6290–6298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantin L. L. The role of sodium current in the radial spread of contraction in frog muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jun;55(6):703–715. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.6.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F. Distribution of potassium and chloride permeability over the surface and T-tubule membranes of mammalian skeletal muscle. J Membr Biol. 1979 Apr 9;45(3-4):293–310. doi: 10.1007/BF01869290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Gage P. W. Ionic conductances of the surface and transverse tubular membranes of frog sartorius fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Mar;53(3):279–297. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser A. F., Lanyi J. K. Structure of the lipid phase in cell envelope vesicles from Halobacterium cutirubrum. Biochemistry. 1973 May 8;12(10):1933–1939. doi: 10.1021/bi00734a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry D. R., Glossmann H. Identification of putative calcium channels in skeletal muscle microsomes. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 8;148(2):331–337. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80835-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., Jaimovich E., Delpont E., Lazdunski M. [3H]nitrendipine labelling of the Ca2+ channel in skeletal muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 17;86(1):141–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., Jaimovich E., Delpont E., Lazdunski M. [3H]nitrendipine receptors in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6086–6092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fretten P., Morris S. J., Watts A., Marsh D. Lipid-lipid and lipid-protein interactions in chromaffin granule membranes. A spin label ESR study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 23;598(2):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. R., Meissner G. Na+, K+, H+ and Cl- permeability properties of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcolemmal vesicles. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 May;223(1):9–23. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90566-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Gains N., Semenza G., Spiess M. Orientation and motion of spin-labels in rabbit small intestinal brush border vesicle membranes. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5621–5628. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Houslay M. D., McGill K. A., Birdsall N. J., Metcalfe J. C., Warren G. B. Annular lipids determine the ATPase activity of a calcium transport protein complexed with dipalmitoyllecithin. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 21;15(19):4145–4151. doi: 10.1021/bi00664a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo C., Gonzalez M. E., Lagos R. Characterization of the Ca2+- or Mg2+-ATPase of transverse tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13937–13945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo C., Thomas D. D., Ikemoto N. Effect of the lipid environment on protein motion and enzymatic activity of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6879–6887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 27;93(2):314–326. doi: 10.1021/ja00731a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida H., Maeda T., Ohki K., Nozawa Y., Ohnishi S. I. Transfer of phosphatidylcholine between different membranes in Tetrahymena as studied by spin labeling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 21;508(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaimovich E., Chicheportiche R., Lombet A., Lazdunski M., Ildefonse M., Rougier O. Differences in the properties of Na+ channels in muscle surface and T-tubular membranes revealed by tetrodotoxin derivatives. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Apr;397(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00585159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaimovich E., Venosa R. A., Shrager P., Horowicz P. Density and distribution of tetrodotoxin receptors in normal and detubulated frog sartorius muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Apr;67(4):399–416. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.4.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith A., Bulfield G., Snipes W. Spin-labeled Neurospora mitochondria. Biophys J. 1970 Jul;10(7):618–629. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86324-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. S., Hopwood L. E., Swartz H. M. Electron spin resonance studies of changes in membrane fluidity of Chinese hamster ovary cells during the cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 16;602(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90294-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. H., Caswell A. H., Brunschwig J. P., Baerwald R. j., Garcia M. Lipid analysis and freeze-fracture studies on isolated transverse tubules and sarcoplasmic reticulum subfractions of skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):540–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. H., Caswell A. H., Brunschwig J. P. Isolation of transverse tubules by fractionation of triad junctions of skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5565–5574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. H., Caswell A. H., Garcia M., Letellier L. Ouabain binding and coupled sodium, potassium, and chloride transport in isolated transverse tubules of skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Sep;74(3):335–349. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.3.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre J. O., Samson P., Brenner S. C., Dalton L., Dalton L., Fleischer S. EPR Studies of the Motional Characteristics of the Phospholipid in Functional Reconstituted Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Membrane Vesicles. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):53–56. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84595-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Schalow G. Transition temperature of excitation-contraction coupling in frog twitch muscle fibres. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):326–328. doi: 10.1038/280326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Onishi S. Organization of lipids in sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane and Ca2+-dependent ATPase activity. J Biochem. 1975 Nov;78(5):1039–1045. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemblatt M., Hidalgo C., Vergara C., Ikemoto N. Immunological and biochemical properties of transverse tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8140–8148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabbadini R. A., Okamoto V. R. The distribution of ATPase activities in purified transverse tubular membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 May;223(1):107–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90576-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scales D. J., Sabbadini R. A. Microsomal T system: a stereological analysis of purified microsomes derived from normal and dystrophic skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):33–46. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier-Muccillo S., Marsh D., Dugas H., Schneider H., Smith C. P. A spin probe study of the influence of cholesterol on motion and orientation of phospholipids in oriented multibilayers and vesicles. Chem Phys Lipids. 1973 Jan;10(1):11–27. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(73)90037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Tamm L., Hymel L., Fleischer S. Deuterium and phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance and fluorescence depolarization studies of functional reconstituted sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3922–3932. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumnicht G. E., Sabbadini R. A. Lipid composition of transverse tubular membranes from normal and dystrophic skeletal muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 May;215(2):628–637. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Bigelow D. J., Squier T. C., Hidalgo C. Rotational dynamics of protein and boundary lipid in sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):217–225. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84671-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


