FIG. 10.
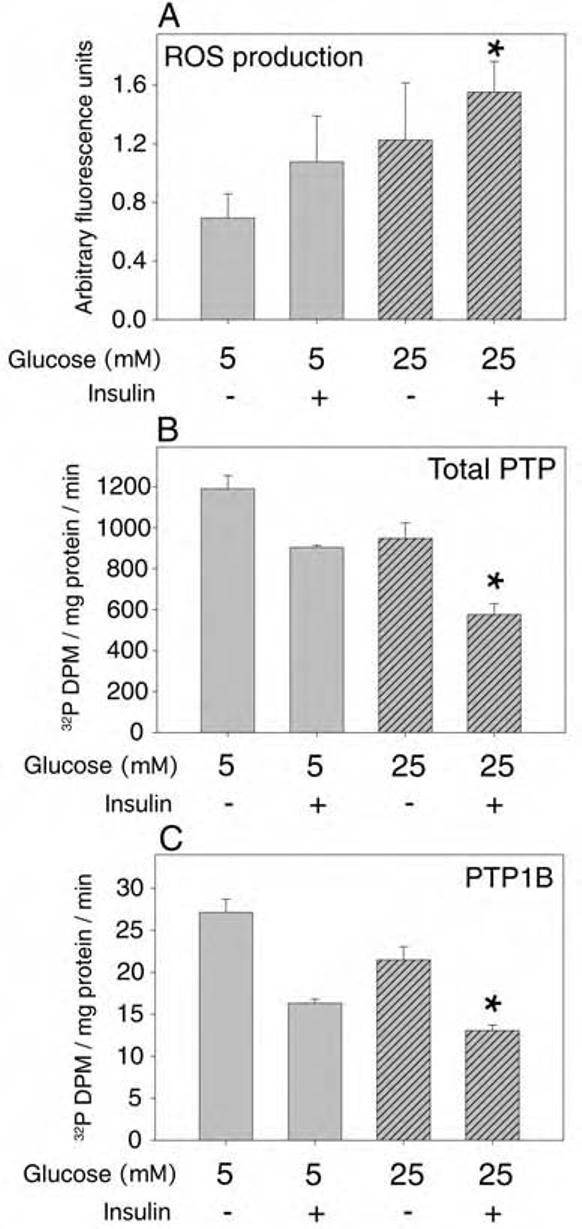
Effect of high glucose and insulin on ROS production and PTP activities in primary cultured rat adipocytes. Primary rat adipocytes were isolated as described in Experimental Procedures and cultured under sterile conditions overnight in DMEM with 0.2% (wt/vol) BSA also containing either 5 mM glucose with 20 mM mannitol or high glucose medium containing mM glucose. (A) Prior to measurement of ROS, the cells were loaded with DCF-DA and, where indicated, stimulated with 100 nM insulin for 5 min followed by flow cytometry analysis. Following the indicated treatments, adipocyte lysates were prepared under anaerobic conditions and the total PTP activity (B) or the specific activity of immunoprecipitated PTP1B (C) was measured by hydrolysis of 32P-RCM-lysozyme, as described in Experimental Procedures. The asterisks indicate a significant difference (p < 0.01) compared with control samples in low glucose without insulin stimulation.
