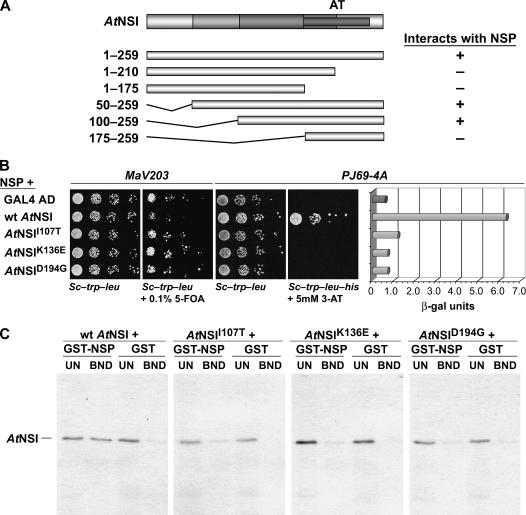
Figure 1.
AtNSI residues 107 to 194 are required for interaction with NSP. A, NSI residues 1 to 99 are not required for interaction with NSP. Schematic diagram of NSI, with acetyltransferase domain (AT) indicated (darkest gray bar), and of NSI truncations tested for interaction with NSP in the yeast two-hybrid assay. The coding region for full-length or each truncated NSI was fused to the GAD in pBI771 and coexpressed in yeast strain PJ69-4A with NSP fused to the GBD in pBI880. +, Interacted with NSP; −, no interaction. B, Missense mutants AtNSII107T, AtNSIK136E, and AtNSID194G are defective in their interaction with NSP. Wild-type NSI, or missense mutants NSII107T, NSIK136E, and NSID194G, each fused to the GAD in pBI771, or plasmid pBI771 (GAL4 AD) were coexpressed with pBI880-NSP in the yeast reverse two-hybrid assay (yeast strain MaV203) or the classic two-hybrid assay (growth in and β-gal assays of extracts from yeast strain PJ69-4A). Increased growth of MaV203 in the presence of 0.1% 5-FOA, and lack of His prototrophy (no growth on SC-Trp-Leu-His) and low β-gal activity for PJ69-4A, show that NSII107T, NSIK136E, and NSID194G are defective in their ability to interact with NSP. C, AtNSII107T, AtNSIK136E, and AtNSID194G are defective in binding to NSP in vitro. Wild-type NSI, or missense mutants NSII107T, NSIK136E, and NSID194G, were labeled with 35S-met by coupled in vitro transcription and translation, and equal amounts were incubated with a standardized amount of GST-NSP or GST alone, each tethered to glutathione-Sepharose. Following washing, bound NSI was analyzed by SDS-PAGE on 12% gels. Approximately 17% of unbound fractions (UN) and all of the bound (BND) fractions were analyzed. Full-length NSI migrates at approximately 34 kD.